Google के Tensor Processing Units उन अधिकांश अत्याधुनिक AI models को power करते हैं जिनसे आप दैनिक रूप से interact करते हैं, फिर भी अधिकतर engineers उनकी architecture से आश्चर्यजनक रूप से अपरिचित हैं। जबकि NVIDIA GPUs developer mindshare पर हावी हैं, TPUs चुपचाप Gemini 2.0, Claude, और दर्जनों अन्य frontier models को उस पैमाने पर train और serve करते हैं जो पारंपरिक GPU infrastructure का उपयोग करके अधिकांश organizations को दिवालिया कर देगा। Anthropic ने हाल ही में भविष्य के Claude models को train करने के लिए दस लाख से अधिक TPU chips deploy करने की प्रतिबद्धता जताई है—जो एक gigawatt से अधिक compute capacity का प्रतिनिधित्व करती है।¹ Google की नवीनतम Ironwood generation 9,216-chip superpods में 42.5 exaflops का FP8 compute deliver करती है, एक पैमाना जो production AI infrastructure के अर्थ को नया आकार देता है।²
TPUs के पीछे की technical sophistication सामान्य performance metrics से कहीं आगे तक फैली है। ये processors GPUs से मौलिक रूप से भिन्न design philosophy को embodied करते हैं, matrix multiplication और tensor operations में extreme specialization के लिए general-purpose flexibility का trade-off करते हैं। Engineers जो TPU architecture को समझते हैं, वे 256×256 systolic arrays का फायदा उठा सकते हैं जो प्रति cycle 65,536 multiply-accumulate operations process करते हैं, embedding-intensive workloads के लिए third-generation SparseCore accelerators का leverage करते हैं, और optical circuit switches को program करते हैं जो 10 nanoseconds से कम में multi-petabit datacenter topologies को reconfigure करते हैं।³ यह architecture transistor-level design decisions से लेकर building-scale supercomputer orchestration तक सब कुछ span करती है।
आगे का technical content सावधानीपूर्वक attention की मांग करता है। हम TPU evolution की सात generations की जांच करते हैं, systolic array mathematics और dataflow patterns को dissect करते हैं, SRAM tiles से HBM3e channels तक memory hierarchies को explore करते हैं, intermediate representation level पर XLA compiler optimizations का analyze करते हैं, और investigate करते हैं कि क्यों collective operations equivalent Ethernet-based GPU clusters की तुलना में 10× तेजी से execute होते हैं।⁴ आप register-level specifications, cycle-accurate performance modeling, और architectural tradeoffs का सामना करेंगे जो TPUs को GPUs की तुलना में एक साथ अधिक powerful और अधिक constrained बनाते हैं। यहां की depth उन engineers की सेवा करती है जो AI infrastructure की अगली generation का निर्माण कर रहे हैं और उन researchers की जो current accelerators की उपलब्धि की boundaries को push कर रहे हैं।
विकास: आर्किटेक्चरल इनोवेशन की सात पीढ़ियां
TPU v1: केवल Inference के लिए स्पेशलाइजेशन (2015)
Google ने 2015 में पहला Tensor Processing Unit deploy किया एक critical समस्या को हल करने के लिए: neural network inference workloads से कंपनी के datacenter footprint के दोगुना हो जाने का खतरा था।⁵ Engineers ने TPU v1 को विशेष रूप से inference के लिए design किया, training capabilities को पूरी तरह हटाकर deployed models के लिए performance और power efficiency को maximize करने के लिए। chip में 8-bit integer multiply-accumulate units का 256×256 systolic array था, जो सिर्फ 28-40 watts thermal design power पर 92 teraops per second deliver करता था।⁶
architecture radical minimalism का प्रतीक था। एक single Matrix Multiply Unit weight-stationary dataflow के माध्यम से INT8 operations process करता था, जहां weights systolic array में fixed रहते थे जबकि activations grid में horizontally stream होते थे। Partial sums vertically propagate होते हैं, पूरे matrix multiplication के लिए intermediate memory writes को eliminate करते हुए। chip, host systems से PCIe के माध्यम से connected था, external memory के लिए DDR3 DRAM पर rely करता था और power efficiency के लिए deliberately conservative 700 MHz पर operate करता था।⁷
Performance gains ने Google के engineers को भी चौंका दिया। TPU v1 ने production inference workloads के लिए contemporary CPUs और GPUs की तुलना में operations per watt में 30× से 80× improvement हासिल की।⁸ chip ने Google Search ranking, 1 billion daily requests process करने वाली translation services, और 2 billion users के लिए YouTube recommendations को handle किया। success ने एक core architectural insight को validate किया: narrow workloads के लिए optimized purpose-built accelerators general-purpose processors से order-of-magnitude improvements deliver कर सकते हैं।
TPU v2: Scale पर Training को Enable करना (2017)
second generation ने TPUs को inference-only accelerators से complete training platforms में transform कर दिया। Google ने floating-point operations के आसपास पूरे architecture को redesign किया, 256×256 INT8 array को per core dual 128×128 bfloat16 multiply-accumulators से replace किया।⁹ हर chip में per core 8GB High Bandwidth Memory share करने वाले दो TensorCores थे, DDR3 से एक massive upgrade जो neural network training की जरूरत के लिए bandwidth प्रदान करता था।
Bfloat16 precision TPU v2 की success के लिए critical साबित हुई। format FP32 के same 8-bit exponent range को maintain करता है जबकि mantissa को 7 bits तक reduce कर देता है, memory bandwidth requirements को half करते हुए training के लिए dynamic range preserve करता है।¹⁰ Engineers ने observe किया कि reduced mantissa precision ने actually many models में generalization improve की regularization के एक form के रूप में act करके, जबकि full FP32 exponent range ने FP16 training को plague करने वाली underflow और overflow issues को prevent किया।
architectural innovation जिसने TPU v2 को truly differentiate किया वह था Inter-Chip Interconnect (ICI)। पिछले accelerators को multi-chip communication के लिए Ethernet या InfiniBand की जरूरत थी, जो latency और bandwidth bottlenecks introduce करते थे। Google ने custom high-speed bidirectional links design किए जो हर TPU को 2D torus topology में चार neighbors से directly connect करते थे।¹¹ interconnect ने 256 chips तक के TPU v2 "pods" को single logical accelerator के रूप में function करने में enable किया, all-reduce जैसे collective operations network-based alternatives से कहीं faster execute करते हुए।
TPU v3: Water-Cooled Performance Scaling (2018)
Google ने TPU v3 में clock speeds और core counts को aggressively push किया, 420 teraflops per chip deliver करते हुए—v2 के performance से दोगुना से भी ज्यादा।¹² increased power density ने एक dramatic architectural change को force किया: liquid cooling। हर TPU v3 pod को water cooling infrastructure की जरूरत थी, पिछली generations के air-cooled designs और अधिकांश datacenter accelerators से departure।¹³
chip ने dual 128×128 MXU architecture को maintain किया लेकिन total number of cores को increase किया और memory bandwidth improve की। हर TPU v3 में दो cores वाले चार chips थे, chips में total 32GB HBM memory share करते हुए।¹⁴ vector processing units को activation functions, normalization operations, और gradient computations के लिए enhancements मिले जो frequently अकेले matrix units पर training को bottleneck करते थे।
Deployments v2 के same 2D torus ICI topology का use करते हुए 2,048-chip pods तक scale हुए लेकिन increased per-link bandwidth के साथ। Google ने v3 pods पर increasingly large models को train किया, discover करते हुए कि torus topology का reduced network diameter (किसी भी दो chips के बीच maximum distance N के बजाय N/2 के रूप में scale करता है) data-parallel और model-parallel training strategies दोनों के लिए communication overhead को minimize करता है।¹⁵
TPU v4: Optical Circuit Switching Breakthrough (2021)
fourth generation ने original TPU के बाद से Google की most significant architectural leap represent की। Engineers ने pod scale को 4,096 chips तक increase किया और interconnect के लिए optical circuit switching (OCS) introduce किया, telecommunications से borrowed एक technology जिसने datacenter-scale ML infrastructure को revolutionize किया।¹⁶
TPU v4 के core architecture में enhanced vector और scalar units के साथ-साथ four 128×128 MXUs per TensorCore था। हर TensorCore pair per-core Vector Memory के अलावा 128MB Common Memory share करता था, अधिक sophisticated data staging और reuse patterns को enable करते हुए।¹⁷ chip topology 2D से 3D torus में evolve हुई, हर TPU को चार के बजाय छह neighbors से connect करते हुए, network diameter को further reduce करते हुए और bisection bandwidth improve करते हुए।
optical circuit switching system ने large-scale deployment के बारे में सब कुछ बदल दिया। TPUs के बीच fixed cabling के बजाय, Google ने programmable optical switches deploy किए जो dynamically reconfigure कर सकते थे कि कौन से chips कौन से से connect होते हैं। MEMS (microelectromechanical systems) mirrors physically light beams को redirect करते हैं arbitrary TPU pairs को एक साथ patch करने के लिए, optical fiber transmission time के beyond essentially zero latency introduce करते हुए।¹⁸ switches sub-10-nanosecond windows में reconfigure होते हैं, अधिकांश network protocol handshakes से faster।
OCS architecture ने पहले impossible capabilities को enable किया। Google चार chips से full 4,096-chip pod तक किसी भी size के "slices" provision कर सकता था optical switches को appropriately program करके। Failed chips को पूरे racks को down किए बिना seamlessly route around किया जा सकता था। Most remarkably, different datacenter locations में physically distant TPUs network topology में logically adjacent हो सकते थे, physical और logical layout को entirely decouple करते हुए।¹⁹
TPU v4 ने SparseCore भी introduce किया, recommendation systems, ranking models, और massive vocabulary embeddings वाले large language models में daily use होने वाले embedding operations को handle करने के लिए एक specialized processor। SparseCore में four dedicated processors per chip थे, हर एक में 2.5MB scratchpad memory और sparse memory access patterns के लिए optimized dataflow था।²⁰ ultra-large embeddings वाले Models ने total chip die area और power budget के सिर्फ 5% use करके 5-7× speedups achieve किए।
TPU v5p और v5e: Specialization और Scale (2022-2023)
Google ने fifth generation को different use cases target करने वाले दो distinct products में split किया। TPU v5p ने large-scale training के लिए maximum performance को prioritize किया, जबकि v5e ने cost-effective inference और smaller training jobs के लिए optimize किया।²¹
TPU v5p ने 8,960-chip pods में approximately 4.45 exaflops per second achieve किया, v4 के maximum pod size से दोगुना से ज्यादा।²² interconnect bandwidth 4,800 Gbps per chip तक पहुंची, और 3D torus topology ने massive 16×20×28 superpods में chips को connect किया। optical circuit switching fabric ने complete v5p superpod को wire करने के लिए 48 OCS units में 13,824 optical ports manage किए, computing history में largest production optical switching deployments में से एक को represent करते हुए।²³
TPU v5e ने different approach लिया, aggressive power और cost targets hit करने के लिए core count और clock speed reduce किया। Inference-optimized chips में दो के बजाय only one TPU core per chip था, और 2D torus topology पर return किया, जो smaller pod sizes के लिए sufficient था।²⁴ architectural simplification ने Google को उन workloads के लिए v5e को competitively price करने में enable किया जहां absolute performance से ज्यादा performance per dollar matter करता था।
TPU v6e Trillium: Matrix Performance को Quadrupling करना (2024)
Trillium ने Matrix Multiply Unit को 128×128 से 256×256 multiply-accumulators तक expand करके another architectural inflection point mark किया।²⁵ larger array ने same clock speed पर FLOPs per cycle को quadruple किया, expanded MXU और increased clock frequencies के combination के माध्यम से TPU v5e से 4.7× peak compute performance deliver किया।
memory subsystem को equally dramatic upgrades मिले। HBM capacity per chip 32GB तक double हुई, next-generation HBM channels द्वारा bandwidth double के साथ।²⁶ Interchip Interconnect bandwidth similarly double हुई, 256 Trillium chips के pods को उन models के लिए higher throughput sustain करने में enable करते हुए जो compute और communication दोनों को stress करते थे।²⁷
Trillium में third-generation SparseCore accelerator था, ranking और recommendation workloads में ultra-large embeddings के लिए enhanced capabilities के साथ। updated design ने memory access patterns improve किए और matrix multiplications के बजाय embedding lookups से dominated models के लिए SparseCores और HBM के बीच adequate bandwidth increase की।²⁸
substantial performance gains के बावजूद Energy efficiency v5e से 67% improve हुई।²⁹ Google ने advanced process nodes, architectural optimizations जो wasted work reduce करते थे, और उन operations के दौरान unused units की careful power gating के माध्यम से efficiency gains achieve किए जो simultaneously chip के सभी parts को stress नहीं करते थे।
TPU v7 Ironwood: FP8 Era (2025)
Google की seventh-generation TPU, codenamed Ironwood, native FP8 support के साथ design की गई first TPU represent करती है और विशेष रूप से "age of inference" के लिए optimized है जबकि state-of-the-art training performance maintain करती है।³⁰ हर Ironwood chip 4.6 petaFLOPS dense FP8 compute deliver करती है—NVIDIA के competing B200 के 4.5 petaFLOPS को slightly exceed करते हुए—जबकि 600W thermal design power pull करती है।³¹
memory system per chip 192GB HBM3e memory तक expand हुआ, Trillium की capacity से six times, bandwidth 7.4TB/s तक पहुंचने के साथ।³² dramatic memory increase ultra-large models को key-value caches के साथ serve करने में enable करती है जिन्हें पहले multiple accelerators में complex tensor parallelism की जरूरत थी। Google ने specifically memory capacity को million-token windows approach करने वाले emerging multi-modal models और long-context applications support करने के लिए design किया।
Ironwood के interconnect चार ICI links के माध्यम से 9.6 Tbps aggregate bidirectional bandwidth provide करते हैं, 1.2 TB/s peak per-chip bandwidth में translate करते हुए।³³ architecture smaller deployments के लिए 256-chip pods से massive 9,216-chip superpods तक scale करती है जो 42.5 FP8 exaflops compute power deliver करती है।³⁴ Google की Jupiter datacenter network technology theoretically single cluster में 43 Ironwood superpods तक support कर सकती थी—roughly 400,000 accelerators जो almost incomprehensible scale of compute represent करते हैं।³⁵
FP8 support precision strategy में fundamental shift represent करता है। Prior TPU generations software techniques का use करके 8-bit operations emulate करती थीं, जो overhead introduce करते थे। Ironwood E4M3 (4-bit exponent, 3-bit mantissa) और E5M2 (5-bit exponent, 2-bit mantissa) formats दोनों support करने वाले native FP8 multiply-accumulate units implement करती है।³⁶ dual format support forward passes के लिए E4M3 mixing enable करता है जहां precision कम matter करती है और backward passes के लिए E5M2 जहां gradient magnitudes maintain करना training instability prevent करता है।
Anthropic की 2026 से शुरू होकर one million से अधिक Ironwood chips deploy करने की commitment architecture की production readiness demonstrate करती है। company Claude models को exclusively train और serve करने के लिए well over a gigawatt TPU capacity leverage करने की plan है।३⁷ scale सबसे significant known GPU deployments को भी dwarf करती है और frontier model development के लिए TPU architecture पर fundamental bet represent करती है।
Current-Generation Quick Reference
निम्नलिखित tables 2025 में production deployments के लिए most relevant तीन current-generation TPUs के लिए scannable specifications provide करती हैं:
Table 1: Core Compute Specifications

Table 2: Memory और Bandwidth
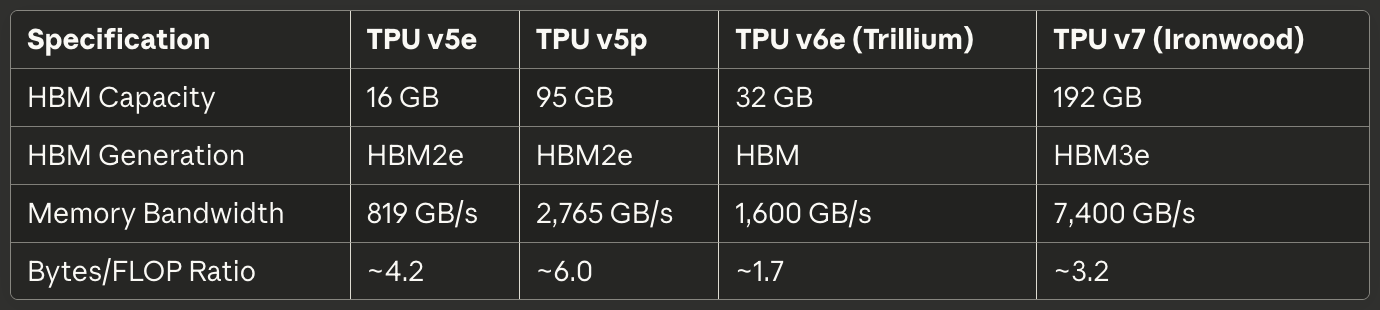
Table 3: Interconnect और Scaling
Table 4: Power और Efficiency

Table 5: Recommended Use Cases

Hardware Architecture: Silicon के अंदर
Systolic Array Mathematics और Dataflow
Matrix Multiply Unit TPU architecture का heart बनाता है, और systolic arrays को समझने के लिए GPU SIMD lanes की तुलना में parallelism के प्रति उनके fundamentally different approach को समझना जरूरी है। एक systolic array multiply-accumulate units को grid में chain करती है जहां data structure के माध्यम से rhythmically flow करता है—इसलिए "systolic," दिल के माध्यम से blood के rhythmic pumping को evoke करते हुए।³⁸
TPU v6e के 256×256 systolic array को consider करें जो matrix multiplication C = A × B perform करती है। Engineers matrix B के weights को 65,536 individual multiply-accumulate units में preload करते हैं जो grid में arranged हैं। Matrix A की activation values left edge से enter होती हैं और array में horizontally flow करती हैं। हर MAC unit अपने stored weight को incoming activation से multiply करता है, ऊपर से आने वाले partial sum में result add करता है, और activation (horizontally) और updated partial sum (vertically) दोनों को neighboring units को pass करता है।³⁹
dataflow pattern का मतलब है हर activation value horizontal dimension traverse करते समय 256 times reuse होती है, और हर partial sum vertically flow करते समय 256 multiplications से contributions accumulate करता है। Critically, सभी intermediate results short wires के माध्यम से adjacent MAC units के बीच directly pass होते हैं memory में round-tripping के बजाय। architecture हर clock cycle 65,536 multiply-accumulate operations perform करती है, और potentially millions operations involve करने वाले entire matrix multiplication के दौरान, zero intermediate values DRAM या even on-chip SRAM को touch करते हैं।⁴⁰
weight-stationary dataflow pattern neural network inference और training में most common case के लिए optimize करता है: same weight matrix के साथ many different activation matrices को repeatedly multiply करना। Engineers weights को once load करते हैं, फिर reloading के बिना unbounded activation batches को array के माध्यम से stream करते हैं। pattern convolutional layers, fully connected layers, और Q·K^T और attention·V operations के लिए exceptionally well काम करता है जो transformer models को dominate करते हैं।⁴¹
Energy efficiency data reuse और spatial locality से stem होती है। DRAM से value read करना single multiply-accumulate operation से roughly 200× ज्यादा energy consume करता है।⁴² हर weight को 256 times और हर activation को memory accesses के बिना 256 times reuse करके, systolic array उन architectures के लिए impossible operations-per-watt ratios achieve करती है जो compute units और memory hierarchies के बीच data shuttle करती हैं।
systolic array की weakness dynamic या irregular computation patterns के साथ emerge होती है। क्योंकि data fixed schedule पर grid के माध्यम से flow करता है, architecture conditional execution, sparse matrices (unless SparseCore use करके), और random access patterns require करने वाले operations के साथ struggle करती है। inflexibility target workload पर extreme efficiency के लिए generality trade करती है: predictable access patterns के साथ dense matrix multiplication।
TensorCore Internal Architecture
हर TPU chip एक या अधिक TensorCores contain करती है—complete processing unit जिसमें Matrix Multiply Unit, Vector Processing Unit, और Scalar Unit concert में काम करते हैं।⁴³ TensorCore fundamental building block represent करता है जिसे software target करता है, और इसके तीन components के बीच interaction समझना TPU performance characteristics और programming patterns दोनों explain करता है।
Matrix Multiply Unit FP32 accumulation के साथ bfloat16 या FP8 inputs पर per cycle 16,000 multiply-accumulate operations execute करता है।⁴⁴ mixed-precision approach accumulator में numerical accuracy preserve करता है जबकि inputs के लिए memory bandwidth reduce करता है। Engineers ने observe किया कि accumulation के दौरान complete FP32 precision maintain करना hundreds या thousands intermediate products sum करते समय catastrophic cancellation errors prevent करता है, जबकि reduced-precision inputs rarely final model quality affect करते हैं।
Vector Processing Unit उन operations को handle करता है जो MXU की rigid structure के लिए poorly suited हैं। Activation functions (ReLU, GELU, SiLU), normalization layers (batch norm, layer norm), softmax, pooling, dropout, और element-wise operations VPU की 128-lane SIMD architecture पर execute होते हैं।⁴⁵ VPU FP32 और INT32 datatypes पर operate करता है, softmax जैसे numerically sensitive operations के लिए required precision provide करते हुए, जहां exponentials और divisions large dynamic ranges create कर सकते हैं।
Scalar Unit पूरे TensorCore को orchestrate करता है। single-threaded processor control flow execute करता है, complex indexing patterns के लिए memory addresses calculate करता है, और High Bandwidth Memory से Vector Memory में DMA transfers initiate करता है।⁴⁶ क्योंकि scalar unit single-threaded run करता है, हर TensorCore per cycle केवल one DMA request create कर सकता है—memory-intensive operations के लिए bottleneck जो MXU या VPU compute throughput saturate नहीं करते।
TensorCore को feed करने वाली memory hierarchy raw compute capability के साथ-साथ achievable performance determine करती है। Vector Memory (VMEM) हर TensorCore के लिए exclusive software-managed scratchpad SRAM के रूप में act करती है, typically tens of megabytes sized। XLA compiler HBM और VMEM के बीच data movement explicitly schedule करता है, decide करते हुए कि fast local memory में क्या stage करना है और कब results को back write करना है।⁴⁷
Common Memory (CMEM), TPU v4 और बाद की generations में present, chip पर सभी TensorCores के लिए accessible larger shared pool provide करती है। TPU v4 architecture ने two TensorCores के बीच shared 128MB CMEM allocate की, अधिक sophisticated producer-consumer patterns enable करते हुए जिसमें एक core के outputs दूसरे core के inputs को HBM में round-tripping के बिना feed करते हैं।⁴⁸
programming model implications enormously matter करते हैं। क्योंकि scalar unit single-threads और vector memory explicit management require करती है, TPU programming modern GPU programming से ज्यादा 1990s-era embedded systems development resemble करती है। CUDA unified memory और hardware-managed caches के साथ memory movement abstract करता है; TPU code (चाहे XLA द्वारा generated हो या Pallas में hand से written) हर data transfer को explicitly orchestrate करना चाहिए। Manual control expert optimization enable करता है लेकिन competent performance के लिए bar raise करता है।
High Bandwidth Memory Architecture
Modern TPUs HBM (High Bandwidth Memory), या HBM3e use करते हैं, CPUs में पाई जाने वाली DDR SDRAM, और कई GPUs में use होने वाली GDDR से radically different memory technology। HBM through-silicon vias (TSVs) use करके multiple DRAM dies को vertically stack करती है, फिर stack को silicon interposer पर processor die के directly adjacent place करती है।⁴⁹ short electrical path और wide interface conventional memory technologies से dramatically higher bandwidth enable करते हैं।
TPU v7 Ironwood 7.4 TB/s की total bandwidth के साथ 192GB HBM3e implement करती है।⁵⁰ memory system multiple channels में divided है, हर एक total capacity के separate portion को independent access provide करते हुए। XLA compiler और runtime को parallel access maximize करने और hotspots avoid करने के लिए HBM channels में tensors को carefully partition करना चाहिए जहां एक channel saturate हो जाती है जबकि अन्य idle बैठती हैं।
memory interface width conventional DRAM को dwarf करती है। जहां DDR5 channel 64 bits width provide कर सकती है, वहीं HBM channel typically 1,024 bits span करती है।⁵¹ extreme width relatively modest clock speeds पर high bandwidth enable करती है, multi-gigahertz frequencies पर narrow interfaces push करने की तुलना में power consumption और signal integrity challenges reduce करते हुए।
Latency characteristics GPU memory systems से substantially differ करती हैं। TPUs small local buffers के beyond hardware-managed caches lack करते हैं, इसलिए architecture compute units की जरूरत से well before software explicitly staging data into VMEM पर rely करती है। caches की lack का मतलब है memory latency directly performance impact करती है unless compiler prefetching और double-buffering के माध्यम से latency को successfully hide करता है।⁵²
Memory capacity limits compute throughput से ज्यादा many workloads को dominate करती हैं। bfloat16 weights के साथ 175-billion parameter model parameters store करने के लिए 350GB require करता है—activations, optimizer states, या gradient buffers के लिए account करने से पहले भी Ironwood के 192GB HBM को already exceed करते हुए। ऐसे models train करना sophisticated techniques demand करता है जैसे gradient checkpointing, multiple chips में optimizer state sharding, और memory footprint minimize करने के लिए parameter updates की careful scheduling।⁵³
TPU runtime MXU efficiency maximize करने के लिए specific tensor layout requirements enforce करती है। क्योंकि systolic array 128×8 tiles में data process करती है, tensors को इन dimensions align करना चाहिए padding waste avoid करने के लिए।⁵⁴ Poorly sized matrices hardware को partial tiles process करने force करती हैं MACs idle बैठने के साथ, directly FLOPS utilization reduce करते हुए। compiler automatically tensors pad और reshape करने attempt करता है, लेकिन model architecture में conscious layout choices substantially performance improve कर सकते हैं।
SparseCore: Specialized Embedding Acceleration
जबकि Matrix Multiply Unit dense matrix operations में excel करता है, embedding-intensive workloads radically different characteristics exhibit करते हैं। Recommendation models, ranking systems, और large language models frequently irregular, data-dependent indices के माध्यम से massive embedding tables (often hundreds of gigabytes) access करते हैं। MXU का structured dataflow इन sparse memory access patterns के लिए कोई advantage provide नहीं करता, SparseCore के specialized architecture को motivate करते हुए।⁵⁵
SparseCore MXU के systolic array से fundamentally different tiled dataflow processor implement करता है। TPU v4 में per chip four SparseCores थे, हर एक में 16 compute tiles।⁵⁶ हर tile local scratchpad memory (SPMEM) और processing elements के साथ independent dataflow unit के रूप में operate करती है। tiles parallel में execute होती हैं, embedding operations के disjoint subsets को simultaneously process करते हुए।
memory hierarchy hot data को small, fast SPMEM में place करती है जबकि full embedding tables को HBM में keep करती है। XLA compiler embedding access patterns analyze करता है determine करने के लिए कि कौन से embedding vectors SPMEM में caching merit करते हैं versus HBM से on demand fetching।⁵⁷ strategy traditional CPU cache hierarchies resemble करती है, लेकिन placement decisions hardware के बजाय software make करता है।
SparseCores directly HBM channels से connect होते हैं, TensorCore के memory path को entirely bypass करते हुए। dedicated connection embedding operations को dense matrix operations के साथ memory bandwidth के लिए compete करने से prevent करती है, दोनों को parallel में proceed करने enable करते हुए।⁵⁸ partitioning उन models के लिए exceptionally well काम करती है जैसे Deep Learning Recommendation Models (DLRMs) जो large embedding lookups के साथ dense neural network layers interleave करते हैं।
mod-sharding strategy target_sc_id = col_id % num_total_sparse_cores compute करके SparseCores में embeddings distribute करती है।⁵⁹ simple sharding function load balancing ensure करती है जब embedding IDs uniformly distributed होते हैं, लेकिन skewed access patterns के लिए hotspots create कर सकती हैं। real-world data के साथ काम करने वाले Engineers को often embedding frequency distributions analyze करने और bottlenecks avoid करने के लिए sharding को manually rebalance करने की जरूरत होती है।
SparseCore से Performance gains MXU और VPU पर identical operations implement करने की तुलना में 5-7× तक पहुंचते हैं, जबकि chip die area और power का केवल 5% consume करते हैं।⁶⁰ dramatic efficiency advantage dense matrix infrastructure के माध्यम से force करने के बजाय sparse operations के लिए purpose-building dataflow से stem होता है। specialization principle TPU architecture के भीतर recursively apply होता है: जैसे TPUs GPUs के general-purpose design से specialize करते हैं, SparseCores TPUs के matrix-oriented design से specialize करते हैं।
Trillium के third-generation SparseCore ने variable SIMD width (FP32 के लिए 8 elements, bfloat16 के लिए 16) introduce किया और memory access patterns improve किए, misaligned reads से wasted bandwidth reduce करते हुए।⁶¹ architectural evolution large language models के larger vocabularies और अधिक sophisticated retrieval-augmented generation patterns trend करने के साथ embedding acceleration में Google के continued investment demonstrate करती है।
इंटरकनेक्ट टेक्नोलॉजी: सुपरकंप्यूटर की वायरिंग
इंटर-चिप इंटरकनेक्ट (ICI) आर्किटेक्चर
इंटर-चिप इंटरकनेक्ट वह महत्वपूर्ण तकनीक है जो TPUs को अलग-थलग एक्सेलेरेटर के बजाय एकीकृत सुपरकंप्यूटर के रूप में कार्य करने में सक्षम बनाती है। GPUs के विपरीत जो Ethernet या InfiniBand नेटवर्क के माध्यम से संचार करते हैं, ICI कस्टम हाई-स्पीड सीरियल लिंक्स को कार्यान्वित करता है जो पड़ोसी TPUs को सीधे जोड़ता है और माइक्रोसेकंड-स्केल लेटेंसी तथा टेराबिट-प्रति-सेकंड बैंडविड्थ प्रदान करता है।⁶²
TPU जेनेरेशन में टोपोलॉजी का विकास पॉड स्केलिंग की बदलती आवश्यकताओं को दर्शाता है। TPU v2, v3, v5e, और v6e 2D torus टोपोलॉजीज को कार्यान्वित करते हैं जिसमें प्रत्येक चिप अपने चार निकटतम पड़ोसियों (उत्तर, दक्षिण, पूर्व, और पश्चिम) से जुड़ता है।⁶³ लिंक्स सीमाओं पर wrap around करते हैं, एक डोनट के आकार की लॉजिकल टोपोलॉजी बनाते हैं जो कम कनेक्शन वाले एज चिप्स को समाप्त कर देती है। 256 TPUs का एक 16×16 ग्रिड इस प्रकार uniform बैंडविड्थ और लेटेंसी विशेषताएं प्रदान करता है चाहे कोई भी दो चिप्स संचार कर रहे हों।
TPU v4 और v5p ने 3D torus टोपोलॉजीज में अपग्रेड किया जिसमें प्रत्येक चिप छह पड़ोसियों से जुड़ता है।⁶⁴ अतिरिक्त आयाम नेटवर्क व्यास को कम करता है—किसी भी दो चिप्स के बीच अधिकतम hop count—लगभग 2√N से 3∛N तक। 4,096-चिप पॉड के लिए, अधिकतम hops लगभग 128 से 48 तक गिर जाते हैं, all-reduce जैसे globally synchronizing operations के लिए worst-case communication latency को काफी कम कर देते हैं।
Toroidal संरचना एक और महत्वपूर्ण लाभ प्रदान करती है: चिप्स में workloads के विभाजन के तरीके की परवाह किए बिना समान bisection bandwidth। कोई भी cut जो torus को आधे में विभाजित करता है, समान संख्या में लिंक्स को पार करता है, उन pathological cases को रोकता है जहां गलत job placement नेटवर्क bottlenecks बनाता है।⁶⁵ Uniform bisection bandwidth scheduling को सरल बनाता है और नीचे चर्चा किए गए optical circuit switch reconfigurability को सक्षम बनाता है।
Bandwidth specifications जेनेरेशन में प्रभावशाली रूप से scale करती हैं। TPU v6e प्रति चिप 13 TB/s की ICI bandwidth प्रदान करता है।⁶⁶ TPU v5p छह 3D torus लिंक्स के माध्यम से प्रति चिप 4,800 Gbps तक पहुंच गया।⁶⁷ Ironwood चार ICI लिंक्स को कार्यान्वित करता है जिसमें 9.6 Tbps aggregate bidirectional bandwidth है, जो प्रति चिप 1.2 TB/s में translate करता है।⁶⁸ तुलना के लिए, एक top-tier 400GbE नेटवर्क इंटरफ़ेस 50GB/s bidirectional bandwidth प्रदान करता है—आधुनिक TPU ICI से एक order of magnitude कम।
racks के भीतर Link technology समान 4×4×4 क्यूब में चिप्स के बीच कम दूरी के लिए direct-attached copper (DAC) cables का उपयोग करती है।⁶⁹ Copper connections synchronized operations execute करने वाले tightly coupled चिप्स के लिए आवश्यक bandwidth प्रदान करते हुए cost और power को minimize करते हैं। Inter-cube और pod-scale लिंक्स optical transceivers में transition करते हैं, datacenter racks को span करने के लिए आवश्यक distance और bandwidth के लिए higher cost और power का trade करते हैं।
Collective operations ICI की अनूठी properties का exploit करते हैं। All-reduce, all-gather, और reduce-scatter operations training के दौरान चिप्स में activations और gradients को frequently synchronize करते हैं। Ethernet-based GPU clusters पर, ये collectives एक hierarchical network को traverse करते हैं जिसमें switches, cables, और network interface cards हैं, प्रत्येक hop पर latency introduce करते हैं। TPU ICI optimized collective algorithms को सीधे hardware में implement करता है, equivalent Ethernet-based GPU implementations की तुलना में all-reduce operations को 10× तेज़ execute करता है।⁷⁰
ऑप्टिकल सर्किट स्विचिंग: डायनामिक टोपोलॉजी रीकॉन्फ़िगरेशन
TPU v4 के साथ optical circuit switching (OCS) की Google की deployment दशकों में datacenter networking में सबसे महत्वपूर्ण innovations में से एक थी। Traditional packet-switched networks—चाहे Ethernet हो या InfiniBand—headers examine करने और appropriate output ports पर forward करने वाले switches के माध्यम से packets को hop-by-hop route करके logical connections establish करते हैं। OCS इसके बजाय endpoints के बीच direct physical light paths बनाने के लिए programmable optical elements का उपयोग करता है, switching latency को पूरी तरह eliminate कर देता है।⁷¹
Core technology MEMS (microelectromechanical systems) mirrors पर निर्भर करती है जो light beams को redirect करने के लिए physically rotate करती हैं। TPU A पर एक transmitter OCS में light भेजता है। OCS के अंदर tiny mirrors उस light beam को TPU B पर receiver तक reflect करने के लिए rotate करती हैं। Connection A से B तक एक direct optical path बन जाता है जिसमें fiber के माध्यम से light propagation के अलावा essentially zero added latency होती है।⁷²
Reconfiguration speed production systems में OCS की practicality निर्धारित करती है। Google की deployment sub-10-nanosecond switching times achieve करती है—typical network protocol round-trip times से तेज़।⁷³ Reconfiguration speed running jobs को disrupt किए बिना या carefully coordinated traffic engineering की आवश्यकता के बिना workload requirements से matching dynamic topology changes को enable करती है।
TPU v5p ने massive scale पर OCS demonstrate किया। Architecture optical circuit switches का उपयोग करती है जो switching fabric में four petabits प्रति सेकंड की aggregate bandwidth deliver करते हैं।⁷⁴ एक single v5p superpod को 16×20×28 3D torus configuration में 8,960 chips को wire करने के लिए 13,824 optical ports manage करने वाली 48 OCS units की आवश्यकता होती है।⁷⁵ Switching system किसी भी computing environment में सबसे बड़ी optical networking deployments में से एक का प्रतिनिधित्व करती है।
OCS traditional networks के साथ असंभव capabilities प्रदान करता है। Physical topology और logical topology पूरी तरह decouple हो जाते हैं—datacenter के विपरीत कोनों में दो TPUs adjacent neighbors के रूप में दिखाई देते हैं यदि OCS direct optical paths बनाता है। Failed chips या links को faulty components को exclude करने और logical torus structure को maintain करने के लिए mirrors को reprogram करके route किया जाता है। New jobs को physically re-cabling racks के बिना appropriate pod configurations बनाने के लिए OCS को program करके किसी भी size के "slices" प्राप्त होते हैं।⁷⁶
Architecture एक single pod से आगे scale करने के लिए Google के Jupiter data center network के साथ integrate करती है। Jupiter Google के custom silicon switches और control plane का उपयोग करके entire datacenters में multi-petabit-per-second bisection bandwidth deliver करता है।⁷⁷ Multiple TPU superpods Jupiter fabric के via connect करते हैं, theoretically 400,000 accelerators तक के clusters को support करते हैं यदि network capacity permit करती है।⁷⁸
Power consumption और reliability characteristics TPU-scale deployments के लिए optical circuit switching का favor करती हैं। Traditional packet switches terabit-per-second rates पर packets को process और forward करने में substantial power consume करते हैं। OCS switches केवल reconfiguration events के दौरान MEMS mirrors को operate करने के लिए power consume करते हैं, फिर idle sit करते हैं, connections stable रहने के दौरान minimal loss के साथ light pass करते हैं।⁷⁹ Architecture की simplicity bugs और performance anomalies के prone complex packet processing और buffering logic को eliminate करके reliability improve करती है।
पॉड आर्किटेक्चर और स्केलिंग विशेषताएं
TPU pods ICI के माध्यम से connected TPUs की सबसे बड़ी single unit का प्रतिनिधित्व करते हैं, एक unified accelerator का निर्माण करते हैं। Physical structure individual chips से trays से cubes से racks से complete pods तक hierarchically build करती है।⁸⁰ Hierarchy को समझना अलग-अलग scales पर memory capacity, communication bandwidth, और fault tolerance के बारे में reasoning के लिए matter करता है।
Fundamental building block एक single tray पर चार chips से consist करता है जो PCIe के via host CPU से connected होते हैं।⁸¹ PCIe connection control plane operations, initial program loading, और training data तथा inference results के लिए infeed/outfeed handle करता है। Distributed training के लिए actual inter-chip communication PCIe के बजाय ICI के माध्यम से flow करता है, PCIe bandwidth bottlenecks से बचता है।
सोलह trays (64 chips) एक single 4×4×4 cube बनाते हैं—pod construction के लिए basic unit। एक cube के भीतर, सभी ICI connections direct-attached copper cables का उपयोग करते हैं क्योंकि chips same rack में short physical distances के साथ reside करते हैं।⁸² Cube wrap-around connections के साथ complete 3D torus implement करता है, एक self-contained 64-chip unit बनाता है जो theoretically independently operate कर सकता है।
TPU v4 pods 64 cubes तक scale करते हैं जिसमें कुल 4,096 chips होते हैं।⁸³ Inter-cube connections optical links में transition करते हैं जो optical circuit switching fabric द्वारा manage किए जाते हैं। OCS इन 4,096 chips को एक single enormous pod, multiple smaller independent pods के रूप में provision कर सकता है, या required होने पर mid-job dynamically reconfigure कर सकता है। Flexibility datacenter operators को different job sizes और priorities में utilization को balance करने में enable करती है।
TPU v5p ने pod scale को 16×20×28 3D torus में 8,960 chips तक push किया।⁸⁴ Specific dimensions careful bandwidth और diameter optimization को reflect करते हैं—network topology के लिए prime factorizations matter करते हैं! Pod 4.45 exaflops का compute deliver करता है और production में deployed सबसे बड़ी single-pod configurations में से एक का प्रतिनिधित्व करता है।
Ironwood smaller deployments के लिए 256-chip pods और massive frontier model training के लिए 9,216-chip superpods दोनों को support करता है।⁸⁵ 9,216-chip configuration 42.5 FP8 exaflops deliver करता है—सिर्फ पांच साल पहले entire Top500 list of supercomputers से भी अधिक compute।⁸⁶ Scale उसे redefine करता है जो organizations pipelined या asynchronous approaches के बजाय synchronous training के साथ accomplish कर सकते हैं।
Scaling efficiency यह निर्धारित करती है कि क्या larger pods actually help करते हैं। Pod size के साथ communication overhead increase करता है क्योंकि chips computing के बजाय synchronizing में अधिक समय spend करते हैं। Google Research ने specific workloads के लिए 32,768 TPUs पर 95% scaling efficiency demonstrate करने वाले results publish किए, मतलब 32,768 TPUs ने उस performance का 95% deliver किया जो perfect linear scaling predict करती।⁸⁷ Efficiency hardware-accelerated collectives, optimized compiler transformations, और gradient synchronization frequency को reduce करने के clever algorithmic approaches से stem करती है।
Pod scale पर fault tolerance sophisticated handling require करती है। Statistical probability हजारों chips के साथ continuously run करने वाली किसी भी system में component failures की guarantee करती है। Optical circuit switch failed components के around reconfigure करके graceful degradation enable करता है। Training checkpointing regular intervals पर occur करती है (typically हर कुछ मिनट), इसलिए job failure को scratch से बजाय केवल last checkpoint से restart करने की आवश्यकता होती है।⁸⁸
सॉफ्टवेयर स्टैक: कंपाइलर्स, फ्रेमवर्क्स, और प्रोग्रामिंग मॉडल्स
XLA Compiler: computation graphs का अनुकूलन
XLA (Accelerated Linear Algebra) TPU के सॉफ्टवेयर स्टैक की आधारशिला है, जो उच्च-स्तरीय फ्रेमवर्क ऑपरेशन्स को TPU पर निष्पादन के लिए अनुकूलित मशीन कोड में संकलित करता है।⁸⁹ यह कंपाइलर सामान्य-उद्देश्य कंपाइलर्स में असंभव आक्रामक अनुकूलन लागू करता है क्योंकि यह machine learning workloads और TPU architecture विशेषताओं के domain knowledge का फायदा उठाता है।
Fusion XLA का सबसे प्रभावशाली अनुकूलन है। कंपाइलर computation graphs का विश्लेषण करके ऑपरेशन्स के अनुक्रमों की पहचान करता है जो intermediate tensors को materialize किए बिना execute हो सकते हैं। एक सरल उदाहरण: element-wise operations जैसे relu(batch_norm(conv(x))) सामान्यतः convolution output को memory में लिखने, batch normalization के लिए इसे पढ़ने, उस परिणाम को memory में लिखने, और ReLU के लिए फिर से पढ़ने की आवश्यकता होती है। XLA इन ऑपरेशन्स को एक single kernel में fuse करता है जो intermediate memory traffic के बिना final ReLU output उत्पन्न करता है।⁹⁰
Fusion का प्रभाव TPU के architecture के साथ बढ़ता है। Memory bandwidth कई workloads को compute throughput से अधिक बाधित करता है—MXU memory system की data feed की तुलना में matrix multiplications तेज़ी से perform कर सकता है। Fusion के माध्यम से intermediate memory writes और reads को समाप्त करना सीधे performance improvements में बदल जाता है, जो अक्सर activation-function-heavy networks के लिए 2× या अधिक speedup प्रदान करता है।⁹¹
Memory layout transformations hardware आवश्यकताओं के लिए tensor storage को अनुकूलित करते हैं। Neural networks अक्सर intuitive indexing के लिए tensors को NHWC format (batch, height, width, channels) में represent करते हैं, लेकिन TPU MXUs उन layouts के साथ सर्वोत्तम perform करते हैं जो 128×8 tiles के साथ align होते हैं।⁹² XLA automatically tensors को transpose, reshape, और pad करता है hardware preferences के अनुसार, केवल आवश्यक स्थानों पर layout transformations insert करता है और कभी-कभी total transformation overhead को minimize करने के लिए preferred layouts को graph के माध्यम से backward propagate करता है।
कंपाइलर sophisticated constant folding और dead code elimination लागू करता है। ML graphs में अक्सर ऐसे subgraphs होते हैं जिनके outputs केवल constants पर निर्भर करते हैं—batch normalization parameters, inference dropout rates, और shape calculations जो प्रति batch के बजाय एक बार execute हो सकते हैं। XLA इन subgraphs को compile time पर evaluate करता है और उन्हें constant tensors से replace करता है, runtime work को कम करता है।⁹³
Cross-replica optimization distributed execution के बारे में knowledge का फायदा उठाता है। जब multiple TPU cores पर training करते हैं, कुछ operations (जैसे batch normalization statistics) सभी replicas में aggregation की आवश्यकता होती है। XLA इन patterns की पहचान करता है और optimized collective operations generate करता है जो explicit message passing के माध्यम से aggregation implement करने के बजाय ICI के hardware-accelerated all-reduce का फायदा उठाता है।⁹⁴
कंपाइलर एक intermediate representation, Mosaic को target करता है, विशेष रूप से TPUs के लिए। Mosaic assembly language से उच्चतर लेकिन input computation graph से निम्न abstraction level पर operate करता है। यह भाषा TPU architectural features जैसे systolic arrays, vector memory, और VMEM staging को expose करती है, जबकि low-level details जैसे instruction scheduling और register allocation को छुपाती है।⁹⁵
Auto-tuning capabilities empirical search के माध्यम से optimal tile sizes और operation parameters का चयन करती हैं। XLA Auto-Tuning (XTAT) system विभिन्न fusion strategies, memory layouts, और tile dimensions को try करता है, प्रत्येक variant के performance को profile करता है, और fastest configuration का चयन करता है।⁹⁶ Complex models के लिए search में substantial compile time लग सकता है, लेकिन counter-intuitive optimizations discover करके dramatic runtime speedups produce करता है जिन्हें humans शायद ही manually identify करते हैं।
JAX: Composable Transformations और SPMD
JAX automatic differentiation, XLA के लिए JIT compilation, और program transformation के लिए first-class support के साथ numerical computation के लिए NumPy-compatible interface प्रदान करता है।⁹⁷ Framework का functional programming paradigm और composable transformation model TPU execution models और distributed parallelism patterns के साथ स्वाभाविक रूप से align होता है।
Core JAX abstraction functions पर mathematical transformations apply करता है। Grad (f) f का gradient compute करता है। Jit (f) f को XLA में JIT-compile करता है। vmap(f) f को नए dimension पर vectorize करता है। महत्वपूर्ण बात यह है कि transformations compose होते हैं: jit(grad(vmap(f))) बिल्कुल अपेक्षित रूप से काम करता है, vectorized gradient function को compile करता है।⁹⁸ Compositional model simple, testable components से complex distributed training loops बनाने में सक्षम बनाता है।
SPMD (Single Program, Multiple Data) JAX के distributed execution model को represent करता है। Programmers कोड लिखते हैं जैसे कि single device को target कर रहे हों, फिर sharding annotations add करते हैं जो indicate करते हैं कि tensors को multiple TPU cores में कैसे partition करना है। XLA compiler और GSPMD (General SPMD) subsystem automatically communication operations insert करते हैं distributed devices पर execute करते समय program semantics को maintain करने के लिए।⁹⁹
Sharding annotations distribution strategies declare करने के लिए PartitionSpec का उपयोग करते हैं। PartitionSpec('batch', None) tensor के पहले dimension को device mesh के 'batch' axis पर shard करता है जबकि दूसरे dimension को replicate करता है। PartitionSpec(None, 'model') दूसरे dimension को partition करके tensor parallelism implement करता है। Annotations को arbitrary tensor ranks और device mesh dimensions के साथ compose किया जा सकता है।¹⁰⁰
GSPMD का automatic parallelization vast amounts के boilerplate code को eliminate करता है। Traditional distributed training के लिए manually full tensors की आवश्यकता वाले operations से पहले all-gather, distributed gradients compute करने के बाद reduce-scatter, और global reductions के लिए all-reduce insert करना आवश्यक होता है। GSPMD sharding specifications का analyze करता है और appropriate collectives को automatically insert करता है, programmers को communication engineering के बजाय algorithm पर focus करने के लिए free करता है।¹⁰¹
Compiler constraint solving का उपयोग करके computation graph के माध्यम से sharding decisions propagate करता है। यदि operation A एक sharded tensor output करता है जिसे operation B consume करता है, GSPMD output के उपयोग के आधार पर B की optimal sharding infer करता है, केवल mathematically आवश्यक स्थानों पर resharding operations insert करता है।¹⁰² Automated inference उस "sharding spaghetti" को prevent करता है जो hand-written distributed code को परेशान करती है।
JAX fine-grained control प्रदान करता है जब automation कम पड़ जाता है। with_sharding_constraint graph locations पर specific sharding को force करता है, automatic inference को override करता है। Custom PJIT (parallel JIT) annotations performance-critical code paths के लिए exact device placement और sharding strategies specify करते हैं। Layered model automatic sharding के साथ rapid prototyping enable करता है जबकि आवश्यक स्थानों पर expert optimization का support करता है।¹⁰³
Shardy 2025 में GSPMD के successor के रूप में emerge हुआ, improved constraint propagation algorithms और dynamic shapes की better handling implement करता है।¹⁰⁴ नया system operation-by-operation के बजाय larger graph regions पर jointly sharding choices के बारे में reasoning करके additional optimization opportunities expose करता है।
PyTorch/XLA: PyTorch को TPUs पर लाना
PyTorch/XLA minimal code changes के साथ PyTorch models को TPUs पर run करने में सक्षम बनाता है, PyTorch के imperative programming model और XLA के graph-based compilation के बीच gap को bridge करता है।¹⁰⁵ Integration PyTorch के developer experience को preserve करने और TPU-specific optimizations को expose करने के बीच संतुलन बनाता है।
मौलिक चुनौती PyTorch के eager execution philosophy से उत्पन्न होती है। PyTorch Python statements execute होने पर तुरंत operations execute करता है, standard tools के साथ debugging enable करता है और natural control flow प्रदान करता है। XLA को compilation से पहले complete computation graphs capture करने की आवश्यकता होती है, जो eager execution और graph compilation के performance benefits के बीच tension पैदा करता है।¹⁰⁶
PyTorch/XLA 2.4 ने eager mode support introduce किया, impedance mismatch को address करता है। Implementation dynamically PyTorch operations को XLA graphs में trace करता है, developers को standard PyTorch code लिखने की अनुमति देता है जबकि अभी भी XLA compilation से benefit होता है।¹⁰⁷ यह mode production deployments के लिए कुछ compilation optimization opportunities को development velocity और debugging simplicity के लिए trade करता है।
Graph mode production deployments के लिए primary path बना रहता है। Developers explicitly functions को XLA compilation के लिए decorators या compilation APIs का उपयोग करके mark करते हैं। Explicit annotations aggressive optimization enable करते हैं लेकिन यह समझने की आवश्यकता होती है कि कौन से operations को single XLA graph में fuse किया जाना चाहिए versus independently execute किया जाना चाहिए।¹⁰⁸
Pallas integration PyTorch/XLA में custom kernel development लाता है। Pallas TPU kernels लिखने के लिए low-level language प्रदान करता है जब XLA का automatic fusion कम पड़ जाता है या specialized operations को hand-optimization की आवश्यकता होती है।¹⁰⁹ यह भाषा TPU memory hierarchy (VMEM, CMEM, HBM) और compute units (MXU, VPU) को expose करती है जबकि raw assembly से higher-level रहती है।
Built-in Pallas kernels performance-critical operations जैसे FlashAttention और PagedAttention implement करते हैं। FlashAttention का tiled attention computation sequence length n के लिए memory bandwidth requirements को O(n²) से O(n) तक कम करता है, models को fixed memory budgets के भीतर much longer sequences process करने में सक्षम बनाता है।¹¹⁰ PagedAttention serving के लिए key-value cache management को optimize करता है, padded implementations की तुलना में 5× speedup achieve करता है।¹¹¹
PyTorch/XLA bridge vLLM TPU के लिए critical साबित हुआ—एक high-performance serving framework जो initially GPUs के लिए design किया गया था। Implementation वास्तव में PyTorch models के लिए भी intermediate lowering path के रूप में JAX का उपयोग करता है, PyTorch frontend compatibility maintain करते हुए JAX के superior parallelism support का फायदा उठाता है।¹¹² Architecture ने 2025 के दौरान initial prototypes की तुलना में 2-5× performance improvements achieve की।
Improvements के बावजूद model compatibility challenges persist करती हैं। कुछ PyTorch operations के XLA equivalents नहीं हैं, CPU execution पर fallback force करते हैं जो performance को degrade करता है। Dynamic control flow graph compilation द्वारा poorly support किया जाता है, अक्सर static, compilable alternatives के साथ dynamic behavior को replace करने के लिए architectural changes की आवश्यकता होती है। PyTorch/XLA repository compatibility document करता है और common problematic patterns के लिए migration guides प्रदान करता है।¹¹³
Precision Formats: BFloat16, FP8, और Quantization
Reduced-precision arithmetic के लिए TPU का support acceptable model quality maintain करते हुए dramatic performance और memory improvements enable करता है। विभिन्न formats के numerical properties को समझना और कब प्रत्येक को apply करना optimal performance achieve करने के लिए critical साबित होता है।¹¹⁴
BFloat16 reduced-precision training पर Google की early bet को represent करता है, पहली बार TPU v2 में appearing। यह format FP32 के 8-bit exponent को maintain करते हुए mantissa को 7 bits (plus sign bit) तक truncate करता है।¹¹⁵ Full exponent range उस underflow और overflow को prevent करती है जिसने early FP16 training को plague किया था, जहाँ gradients अक्सर FP16 की representable range से escape हो जाते थे।
Reduced mantissa quantization error introduce करता है लेकिन शायद ही कभी final model quality को impact करता है। Engineers ने observe किया कि bfloat16 में trained models typically FP32-trained baselines को statistical noise के भीतर match करते हैं, संभवतः इसलिए कि quantization regularization के एक रूप के रूप में काम करता है, tiny numerical details पर overfitting prevent करता है।¹¹⁶ यह format FP32 की तुलना में memory bandwidth और capacity requirements को halve करता है, memory-bound workloads पर performance gains में directly translate करता है।
FP8 reduced precision को further ले जाता है, weights और activations को 8 bits तक compress करता है। दो standard encodings exist करते हैं: E4M3 (4-bit exponent, 3-bit mantissa) forward passes के लिए precision को prioritize करता है, जबकि E5M2 (5-bit exponent, 2-bit mantissa) backward passes के लिए range को prioritize करता है जहाँ gradient magnitudes widely vary करते हैं।¹¹⁷ Ironwood दोनों formats के लिए native FP8 support implement करता है, जबकि earlier TPUs software transformations के माध्यम से FP8 को emulate करते थे।¹¹⁸
Training के दौरान quantization awareness FP8 की numerical success enable करती है। Scratch से FP8 के साथ trained models या FP8-aware techniques के साथ fine-tuned models weight distributions सीखते हैं जो format की limited precision को tolerate करते हैं। Post-training quantization (training के बाद FP32 models को FP8 में convert करना) अक्सर careful calibration के बिना quality को degrade करता है।¹¹⁹
INT8 quantization और भी greater memory savings और inference speedups deliver करता है। Google का Accurate Quantized Training (AQT) TPUs पर bfloat16 baselines की तुलना में minimal quality loss के साथ INT8 training enable करता है।¹²⁰ यह technique scratch से quantization-aware training apply करती है, models को post-training approximation के बजाय learning के दौरान INT8 की constraints के लिए adapt करने की अनुमति देती है।
Mixed-precision strategies formats को strategically combine करती हैं। Forward passes activations और weights के लिए FP8 का उपयोग कर सकते हैं, backward passes gradients के लिए FP8 E5M2 या bfloat16 का उपयोग करते हैं, और optimizer states weight updates के दौरान numerical stability के लिए FP32 में remain करते हैं।¹²¹ Mixed approach speed, memory, और accuracy को balance करता है, अक्सर 4× faster run करते हुए FP32 quality का 90%+ achieve करता है।
Precision tradeoffs speed और memory से आगे numerical stability considerations तक extend होते हैं। Batch normalization, layer normalization, और softmax reduced precision में careful numerical handling require करते हैं। Softmax में large exponentials FP8 या bfloat16 ranges को overflow कर सकते हैं; exponentiation से पहले maximum logit subtract करना mathematical equivalence maintain करते हुए overflow prevent करता है।¹²² XLA compiler safe होने पर इन transformations को automatically implement करता है, लेकिन custom operations को कभी-कभी manual numerical engineering की आवश्यकता होती है।
## प्रोग्रामिंग मॉडल और पैरेललिज़्म रणनीतियाँ
SPMD और Automatic Partitioning
Single Program, Multiple Data (SPMD) पैराडाइम मौलिक रूप से यह आकार देता है कि प्रोग्रामर TPU execution के बारे में कैसे सोचते हैं। कई प्रक्रियाओं को coordinate करने के लिए explicit message-passing कोड लिखने के बजाय, developers एक single program लिखते हैं और annotate करते हैं कि डेटा को devices में कैसे partition किया जाना चाहिए।¹²³ Compiler distribution, communication, और synchronization की mechanical विवरणों को handle करता है।
GSPMD (General SPMD) XLA में automatic partitioning logic को implement करता है। यह system tensor sharding annotations और computation graph structure का विश्लेषण करता है यह निर्धारित करने के लिए कि operations कहाँ किन devices पर execute होते हैं और सही semantics बनाए रखने के लिए किस communication की आवश्यकता है।¹²⁴ यह automation hand-written distributed code में common bugs की पूरी categories को eliminate करता है—mismatched tensor shapes, incorrect collective operation orderings, और improper synchronization से deadlocks।
Compiler का constraint propagation engine minimal annotations से sharding decisions का अनुमान लगाता है। केवल model के input और output sharding को annotate करना अक्सर पर्याप्त होता है; GSPMD intermediate operations के माध्यम से constraints को propagate करता है और automatically efficient distributions select करता है।¹²⁵ जब किसी operation के लिए कई valid shardings मौजूद हों, तो compiler alternatives की communication costs का estimate करता है और lowest-cost option select करता है।
Advanced optimizations communication को computation के साथ overlap करते हैं। All-reduce operations जो replicas में gradients को synchronize करते हैं, वे first layer के gradients complete होने के तुरंत बाद शुरू हो सकते हैं, subsequent layers के backward passes के parallel में execute होते हुए।¹²⁶ Compiler automatically collectives को schedule करता है maximum overlap के लिए, sequential execution की तुलना में adequate communication time को 2× या अधिक कम करता है।
Rematerialization computation को memory के लिए trade करता है। Gradient computation के लिए सभी forward pass activations को store करने के बजाय, compiler selectively activations को backward passes के दौरान recompute करता है जब memory pressure thresholds से अधिक हो जाता है।¹²⁷ यह tradeoff TPUs पर विशेष रूप से अच्छा काम करता है जहाँ compute अक्सर memory bandwidth को outpace करता है, recomputation को memory traffic से सस्ता बनाता है।
Data Parallelism, Tensor Parallelism, और Pipeline Parallelism
Data parallelism सबसे सरल distributed training strategy का प्रतिनिधित्व करता है: पूरे model को N devices में replicate करें और प्रत्येक replica पर अलग-अलग data batches process करें। Locally gradients compute करने के बाद, एक all-reduce replicas में gradients को aggregate करता है, और सभी devices identical weight updates apply करते हैं।¹²⁸ यह approach तब तक linearly scale करता है जब तक communication time computation time पर dominate नहीं करता—typically Ethernet networking के साथ 1,000 GPUs के आसपास लेकिन ICI के साथ 10,000+ TPUs।¹²⁹
Tensor parallelism (जिसे model parallelism भी कहते हैं) individual operations को devices में partition करता है। एक matrix multiplication Y = W @ X weight matrix W को devices में split करता है, जहाँ प्रत्येक output का एक portion compute करता है।¹³⁰ यह strategy parameter storage और computation distribute करके single-device memory से अधिक models को train करने में enable करती है।
Tensor parallelism के लिए communication pattern data parallelism से significantly अलग होता है। हर layer के बाद all-reduce के बजाय, tensor parallelism को पूरे tensors की आवश्यकता वाले operations से पहले all-gather और distributed computations के बाद reduce-scatter की आवश्यकता होती है।¹³¹ Communication volume parameter size के बजाय model activation size के साथ scale करता है, data parallelism से अलग bottlenecks बनाता है।
Pipeline parallelism sequential model layers को devices में partition करता है, अलग-अलग micro-batches को अलग-अलग stages पर simultaneously process करता है। GPipe ने memory usage को bound करते हुए pipeline utilization को maximize करने के लिए careful scheduling के साथ इस strategy को introduce किया।¹³² प्रत्येक device एक micro-batch का forward pass process करता है, activations को next stage में send करता है, फिर next micro-batch को process करता है—एक pipeline बनाता है जहाँ initial ramp-up के बाद सभी devices continuously काम करते हैं।
Gradient staleness pipeline parallelism को complicate करता है। Devices उन gradients का उपयोग करके weights update करते हैं जो potentially दर्जनों micro-batches पुराने activations से compute किए गए हैं, staleness बनाते हैं जो convergence को harm कर सकती है।¹³³ PipeDream जैसे sophisticated scheduling algorithms high throughput maintain करते हुए staleness को minimize करते हैं, और empirical results demonstrate करते हैं कि अधिकांश models quality degradation के बिना moderate staleness को tolerate करते हैं।
3D parallelism तीनों strategies को combine करता है। Data parallelism "data" dimension में distribute करता है, tensor parallelism "model" dimension में, और pipeline parallelism "pipeline" dimension में।¹³⁴ Model architecture, hardware topology, और communication costs के आधार पर dimensions को carefully balance करना throughput को maximize करता है। GPT-3-scale models commonly 3D parallelism का उपयोग करते हैं जिसमें 8-16 replicas में data parallelism, 4-8 GPUs में tensor parallelism, और 4-16 stages में pipeline parallelism होती है।
Sharding Strategies और Optimization
Sharding strategies select करने के लिए mathematical operations और उनकी data dependencies को समझना आवश्यक है। Matrix multiplication C = A @ B कई valid shardings permit करता है: A और B दोनों को replicate करें और partial results compute करें (computation से पहले communication), B को column-wise shard करें और results gather करें (computation के बाद communication), या A को row-wise और B को column-wise shard करें बिना communication के लेकिन smaller per-device matrices के साथ।¹³⁵
Collective operation costs optimal strategies determine करती हैं। All-reduce costs tensor size के साथ linearly scale करती हैं लेकिन tree-based या ring-based reduction algorithms का उपयोग करके device count के साथ sublinearly:¹³⁶ All-gather और reduce-scatter अलग scaling properties exhibit करते हैं। Compiler इन costs को model करता है और total communication time को minimize करने वाली sharding strategies select करता है।
Sequence parallelism large language models के लिए critical के रूप में emerge होता है। Attention mechanisms memory bottlenecks बनाते हैं क्योंकि key-value caches sequence length और batch size के साथ grow करते हैं। Sequence dimension के साथ partitioning memory burden को devices में distribute करता है जबकि केवल attention computation के लिए ही communication introduce करता है।¹³⁷
Expert parallelism Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) models को handle करता है जहाँ अलग-अलग experts अलग-अलग tokens process करते हैं। Sharding strategy shared layers को सभी devices में replicate करती है लेकिन experts को partition करती है, हर token को उसके designated expert device पर route करती है।¹३⁸ Dynamic routing irregular communication patterns बनाता है जो traditional collective operations को challenge करता है, latency और load imbalance को minimize करने के लिए sophisticated runtime systems की आवश्यकता होती है।
Optimizer state sharding large models के लिए memory overhead को कम करता है। Adam जैसे optimizers हर parameter के लिए momentum और variance statistics store करते हैं, जो parameters के लिए आवश्यक memory requirements को triple कर देता है। Parameters को replicated रखते हुए optimizer states को devices में shard करना fixed memory budgets के भीतर larger models को train करने में enable करता है।¹³⁹ इस strategy को weight computations के दौरान optimizer state updates को gather करना आवश्यक होता है लेकिन per-device memory footprint को substantially कम करता है।
Performance Analysis और Benchmarking
MLPerf Results और Competitive Positioning
MLPerf AI accelerator performance को training और inference workloads में measure करने के लिए industry-standard benchmarks प्रदान करता है। Google नियमित रूप से TPU results submit करता है जो competitive performance demonstrate करते हैं, और generations के evolution में clear architectural improvements दिखते हैं।¹⁴⁰
TPU v5e ने 9 में से 8 MLPerf training categories में leading results achieve किए।¹⁴¹ यह breadth सिर्फ large language models से beyond architectural versatility demonstrate करती है—computer vision, recommendation systems, और scientific computing workloads में competitive performance। BERT training NVIDIA A100 GPUs से 2.8× faster complete हुई, transformer-optimized architecture को validate करते हुए।¹⁴²
MLPerf Training v5.0, जो June 2025 में announce हुआ, ने एक Llama 3.1 405B benchmark introduce किया जो suite में largest model को represent करता है।¹⁴³ यह benchmark multi-node scaling, communication overhead, और memory capacity को previous tests से ज्यादा stress करता है। Google Cloud ने TPU submissions के साथ participate किया, हालांकि detailed performance comparisons official results के publication के pending embargoed रहते हैं।
MLPerf Inference v5.0 में चार new benchmarks शामिल थे: Llama 3.1 405B, low-latency applications के लिए Llama 2 70B, RGAT graph neural networks, और 3D object detection के लिए PointPainting।¹⁴⁴ यह diversity accelerators को conventional transformer workloads से beyond emerging application domains में push करती है जहाँ architectural assumptions अलग हो सकते हैं।
Inference benchmarks विशेष रूप से TPU की architectural strengths को favor करते हैं। Batch inference workloads MXU की massive parallelism का leverage करते हैं, transformer serving के लिए competing accelerators से 4× higher throughput achieve करते हुए।¹⁴⁵ Single-query latency TPU की deterministic execution और thermal throttling की absence से benefit करती है, कुछ GPU deployments को plague करने वाली performance variance के बिना consistent latency deliver करते हुए।
Energy efficiency metrics TPU advantages को generations में expand करते हुए दिखाते हैं। TPU v4 ने TPU v3 से 2.7× better performance per watt demonstrate किया, और Trillium ने v5e से 67% improvement दिखाई।¹⁴⁶ Ironwood significantly higher absolute performance के बावजूद Trillium से 2× better performance per watt claim करता है।¹⁴⁷ ये efficiency gains thousand-chip pods में compound होते हैं, datacenter operational costs में millions of dollars में translate होते हुए।
Real-World Training और Inference Performance
Production workloads synthetic benchmarks से absent performance characteristics reveal करते हैं। Google internal services से results publish करता है जो real usage patterns और scaling requirements के under TPU behavior demonstrate करते हैं।¹⁴⁸
ResNet-50 ImageNet training TPU pods पर 28 minutes में complete होती है, computer vision workload performance के लिए एक widely-cited benchmark।¹⁴⁹ Time-to-accuracy metric complete training process capture करता है, जिसमें data loading, augmentation, distributed gradient synchronization, और checkpoint saving शामिल है—सिर्फ theoretical FLOPs नहीं।
T5-3B language model training transformer architectures पर TPU advantages demonstrate करती है। 3-billion-parameter model TPU pods पर 12 hours में train होता है, equivalent GPU configurations पर 31 hours के compared।¹⁵⁰ 2.6× speedup hardware-accelerated attention operations, efficient memory bandwidth utilization, और optimized collective communications से stem करता है।
GPT-3 scale workloads (175B parameters) TPUs पर contemporary GPUs से 1.7× faster time-to-accuracy achieve करते हैं।¹⁵¹ Performance gap larger models के लिए widen होता है, जहाँ memory capacity और bandwidth critical constraints बन जाते हैं। Ironwood का 192GB HBM3e ऐसे models serve करने में enable करता है जिनके लिए lower-memory alternatives पर complex tensor parallelism की जरूरत होती है।
Scaling efficiency measurements enormous scales तक near-linear speedup demonstrate करते हैं। Google Research ने specific transformer training workloads के लिए 32,768 TPUs पर 95% scaling efficiency report की।¹⁵² इस metric का मतलब है कि 32,768 TPUs ने perfect linear scaling predict करने वाले performance का 95% deliver किया—communication overhead scale के साथ increase होने के given remarkable।
FLOPS utilization metrics reveal करते हैं कि workloads available compute को कितनी effectively leverage करते हैं। Transformer models typically TPUs पर 90% FLOPS utilization achieve करते हैं, मतलब theoretical peak performance का 90% actual work में translate होता है।¹⁵³ High utilization operation fusion से memory bottlenecks eliminate करने, large-matrix multiplications में systolic-array efficiency, और compiler optimizations जो wasted cycles minimize करते हैं से stem करता है।
Production inference services billions of queries per day में sustained performance demonstrate करती हैं। Google Translate TPUs पर daily 1 billion requests process करता है।¹⁵⁴ YouTube recommendations TPU-accelerated models use करके 2 billion users serve करते हैं।¹⁵⁵ Google Photos search और organization features के लिए monthly 28 billion images analyze करता है।¹⁵⁶ Operational scale research prototype deployments से beyond reliability और cost-efficiency validate करता है।
Energy Efficiency और Total Cost of Ownership
Power consumption data center operational costs और environmental sustainability को directly impact करता है। TPU की energy efficiency improvements generations में operational expenses और carbon emissions दोनों को scale पर reduce करते हैं।¹⁵⁷
TPU v4 ने 250W TDP specification के बावजूद production workloads में average केवल 200W power draw दिखाया।¹⁵⁸ Average और peak power के बीच headroom flexible thermal design और provisioning enable करता है। GPUs के साथ contrast करें, जहाँ sustained workloads अक्सर TDP limits hit करते हैं, conservative rack power budgets require करते हुए।
Ironwood का 600W TDP previous generations से higher absolute power represent करता है लेकिन dramatically more compute per watt deliver करता है।¹⁵⁹ Per chip 4.6 PFLOPS FP8 performance approximately 7.7 TFLOPS per watt yield करता है—equivalent workloads पर contemporary GPU efficiency के साथ competitive या exceeding।
Datacenter power usage effectiveness (PUE) chip-level efficiency को amplify करता है। Google के TPU data centers 1.1 का PUE achieve करते हैं, मतलब cooling, power conversion, और networking के लिए chip consumption से beyond केवल 10% power overhead।¹⁶⁰ Industry average PUE 1.5 से 2.0 तक range करता है, जहाँ infrastructure overhead के लिए 50-100% additional power जाता है। Low PUE advanced cooling systems, efficient power delivery, और ML workloads के लिए optimize करने वाले deliberate datacenter design से stem करता है।
Carbon intensity considerations energy sources include करने के लिए power से beyond extend होती हैं। Google renewable energy procurement और carbon offset programs के through carbon-neutral power पर TPU datacenters operate करता है।¹⁶¹ Carbon accounting उन organizations के लिए increasingly matter करती है जो cloud computing से Scope 2 emissions track करती हैं।
Total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis में acquisition costs, power consumption, cooling requirements, और maintenance expenses account करना होता है। TPU deployments commonly equivalent GPU installations के compared 20-30% TCO reductions show करते हैं, मुख्य रूप से superior performance per watt और reduced cooling complexity से driven।¹⁶²
Cooling infrastructure costs power density के साथ non-linearly scale करते हैं। Air-cooled racks typically exotic cooling solutions require करने से पहले 15-20kW per rack पर top out करते हैं। High-power GPUs इन limits को push करते हैं, कभी-कभी substantially higher capital और operational costs के साथ liquid cooling infrastructure necessitate करते हुए। TPU की efficiency अधिक deployments को air-cooling range के within रखती है, datacenter design को simplify करते हुए।¹⁶³
तकनीकी लाभ: जहाँ TPUs श्रेष्ठ हैं
Hardware-Accelerated Collective Operations
TPU ICI में विशेषज्ञ collective operation support पारंपरिक networked accelerators पर सबसे महत्वपूर्ण लाभों में से एक प्रदान करता है। All-reduce, distributed training में gradients को synchronize करने के लिए मुख्य operation, TPU ICI पर equivalent Ethernet-based GPU implementations की तुलना में 10× तेज़ execute होता है।¹⁶⁴
Performance gap architectural integration से उत्पन्न होता है। Ethernet-based collectives कई layers से गुजरते हैं: application code collective library (NCCL, Horovod, आदि) को invoke करता है, जो packets generate करती है जो network stack को सौंपे जाते हैं, जो data को NIC में transfer करता है, जो wire पर serialize करता है, switches से गुजरता है, receiving NICs पर deserialize होता है, और प्रक्रिया को reverse करता है। हर layer latency जोड़ती है, memory hierarchies के माध्यम से data copy करती है, और protocol processing के लिए CPU cycles consume करती है।¹⁶⁵
TPU ICI collectives को hardware में implement करता है बिना software layer से गुजरे। Operation सीधे TensorCore से initiate होता है, dedicated ICI links पर data stream करता है, और host CPU को involve किए बिना complete होता है। Direct hardware path उस overhead को eliminate करता है जो traditional implementations में dominant है।¹⁶⁶
Optical circuit-switch topology optimal collective algorithms को enable करती है। Ring-based all-reduce को N devices के लिए केवल 2(N-1) messages की आवश्यकता होती है, और torus topology shortest-path routing provide करती है, latency को minimize करते हुए।¹⁶⁷ Uniform bisection bandwidth hotspots को prevent करती है जहाँ poorly-routed collectives network links को congest करते हैं।
Unified Memory Space और Simplified Programming
TPU का unified memory model GPUs की complex memory hierarchies की तुलना में programming को simplify करता है। Programmers host RAM, GPU global memory, shared memory, और register files के बीच transfers को manage करने के बजाय एक single HBM pool के बारे में सोचते हैं। Simplified model bugs को reduce करता है और faster development velocity enable करता है।¹⁶⁸
Memory fragmentation एक चिंता के रूप में गायब हो जाता है। GPUs fragmented heap से memory allocate करते हैं, जहाँ समय के साथ allocations और deallocations ऐसे holes create करते हैं जिन्हें compaction की आवश्यकता होती है। Compiler के static analysis के via TPU memory management runtime fragmentation को पूर्णतः avoid करता है—tensors को computation graph के आधार पर predetermined locations assign किए जाते हैं।¹⁶⁹
Programming model CUDA errors के पूरे classes को eliminate करता है। Incorrect pointer arithmetic से कोई और "illegal memory access" नहीं, CPU और GPU के बीच कोई cache coherency bugs नहीं, missing cudaDeviceSynchronize() calls से कोई synchronization errors नहीं। Higher-level abstraction CUDA programming में common footguns को prevent करता है।¹⁷⁰
Deterministic Execution और Reproducibility
Floating-point non-associativity parallel computing में reproducibility challenges create करती है। Expression (a + b) + c rounding errors के कारण a + (b + c) से different results दे सकती है, और parallel reductions race conditions के आधार पर runs में different orders में sum कर सकते हैं।¹⁷¹
TPU execution typical GPU implementations की तुलना में stronger determinism exhibit करता है। Systolic array का fixed dataflow pattern runs में identical operation ordering ensure करता है। Collective operations arrival order पर based opportunistic aggregation के बजाय deterministic reduction trees follow करते हैं। Predictability reproducible training enable करती है जहाँ identical hyperparameters और data bit-identical model weights produce करते हैं।¹⁷²
Debugging determinism से enormously benefit करता है। Non-deterministic training failures को root-cause करना nearly impossible बनाता है—क्या NaN genuine algorithmic bug से है या random race condition से? Deterministic execution का मतलब है कि failures reliably reproduce होते हैं, systematic debugging approaches enable करते हुए।¹⁷³
Scientific computing applications विशेष रूप से reproducibility को value करते हैं। Climate models, drug discovery simulations, और physics research verifiable results require करते हैं जो different researchers को identical outcomes reproduce करने की अनुमति देते हैं। TPU का determinism racing non-deterministic alternatives की तुलना में scientific method को better support करता है।¹⁷⁴
Compiler Optimizations और Developer Productivity
XLA का aggressive optimization manual tuning के बिना "out of the box" substantial performance improvements deliver करता है। Researchers eager execution frameworks की तुलना में केवल compilation से model throughput में 40% improvements report करते हैं।¹⁷⁵ Performance free में आती है—कोई kernel engineering required नहीं।
Fusion optimization विशेष रूप से developers को benefit करता है। CUDA में hand-fusing operations custom kernels लिखने, correctness test करने, और framework versions में code maintain करने की आवश्यकता होती है। XLA automatically operations को fuse करता है और update करता है, और models evolve होने पर fusion strategies को adapt करता है, maintenance burden को eliminate करते हुए।¹⁷⁶
Layout transformation automation manual optimization के weeks save करता है। GPU के लिए optimal tensor layouts determine करने में different arrangements को profile करना, manually transposes insert करना, और carefully memory allocation patterns manage करना require होता है। XLA layouts को automatically try करता है और fastest को select करता है, developers को low-level performance engineering के बजाय model architecture पर focus करने की स्वतंत्रता देते हुए।¹⁷⁷
Productivity gain research teams के लिए compound होता है। Infrastructure optimization पर saved time scientific progress को accelerate करता है, more experiments और faster iteration cycles enable करते हुए। Organizations GPU CUDA programming से TPU JAX-based workflows पर move करते समय 3× development velocity improvements report करते हैं।¹⁷⁸
## तकनीकी सीमाएं और नुकसान
प्लेटफॉर्म Lock-In और On-Premises बाधाएं
TPU पहुंच केवल Google Cloud Platform के माध्यम से उपलब्ध है, जो on-premises deployment को रोकती है और vendor lock-in की चिंताओं को बढ़ाती है।¹⁷⁹ डेटा संप्रभुता आवश्यकताओं, air-gapped नेटवर्क, या public cloud के विरुद्ध नीतियों वाले संगठन तकनीकी श्रेष्ठता के बावजूद TPU का लाभ नहीं उठा सकते।
यह बाधा तब और भी महत्वपूर्ण हो जाती है जब AI महत्वपूर्ण infrastructure बन जाता है। एकल cloud provider पर निर्भरता business continuity जोखिम पैदा करती है—मूल्य निर्धारण में परिवर्तन, availability में व्यवधान, या सेवा बंद होना महंगे migrations को मजबूर कर सकता है।¹⁸⁰ कई vendors से GPUs की उपलब्धता (NVIDIA hardware जो AWS, Azure, GCP, और on-prem पर चलता है) वे विकल्प प्रदान करता है जिन्हें TPU architecturally रोकता है।
Multi-cloud रणनीतियों में बाधाएं आती हैं। TPU पर मानकीकरण करने वाले संगठन models को retrain किए बिना या विभिन्न accelerator architectures के लिए अलग codebases maintain किए बिना आसानी से अन्य clouds में burst नहीं कर सकते या multi-cloud redundancy लागू नहीं कर सकते।¹⁸¹ Hybrid GPU/TPU deployments की operational जटिलता अक्सर optimal accelerator selection से cost savings से ज्यादा होती है।
CUDA Ecosystem परिपक्वता अंतर
NVIDIA के CUDA platform ने 15+ वर्षों का ecosystem विकास, libraries, documentation, और community knowledge संचित किया है जिसकी TPU बराबरी नहीं कर सकता।¹⁸² परिपक्वता अंतर TPU adoption के लिए कई pain points में प्रकट होता है।
Library availability व्यापक रूप से CUDA के पक्ष में है। Computer graphics, molecular dynamics, computational fluid dynamics, और genomics जैसे specialized domains ने पिछले दशकों में हजारों CUDA-optimized libraries संचित की हैं। TPU समकक्ष अक्सर exist नहीं करते, जिससे या तो CPU fallback की आवश्यकता होती है (जो performance को नष्ट कर देता है) या महीनों के porting effort की।¹⁸³
Community support के मामले में orders of magnitude का अंतर है। Stack Overflow में विस्तृत उत्तरों के साथ सैकड़ों हजारों CUDA प्रश्न हैं—GitHub repositories की संख्या लाखों में है। Conference talks, academic papers, और blog posts मुख्यतः CUDA programming पर केंद्रित हैं। TPU programmers को तुलनात्मक रूप से sparse resources, लंबे debugging cycles, और परामर्श के लिए कम experts का सामना करना पड़ता है।¹⁸⁴
Educational materials और tutorials व्यापक रूप से CUDA को target करते हैं। University courses CUDA का उपयोग करके GPU programming सिखाते हैं। Online courses CUDA पर केंद्रित हैं। Talent pipeline TPU experts की तुलना में कहीं अधिक CUDA-experienced engineers पैदा करती है, जो hiring और training challenges बनाती है।¹⁸⁵
Custom kernel development ecosystem gap का उदाहरण है। Optimized CUDA kernels लिखना अभी भी nontrivial है लेकिन व्यापक documentation, profiling tools, और example code से लाभ होता है। Pallas custom TPU kernels को enable करता है, लेकिन कम mature tooling और छोटे knowledge base के साथ। Learning curve सबसे performance-critical optimizations को छोड़कर सभी को discourage करती है।¹⁸⁶
Workload विशेषीकरण और लचीलेपन की बाधाएं
TPU की architecture specific workload patterns के लिए optimize करती है—मुख्यतः dense matrix multiplication with regular access patterns और large batch sizes। Sweet spot के बाहर के operations में performance cliffs का सामना करना पड़ता है।¹⁸⁷
Dynamic shapes TPU execution models को challenge करते हैं। XLA compiler optimization और code generation के लिए fixed tensor dimensions मानता है। Variable sequence lengths, dynamic control flow, या data-dependent shapes वाले models को maximum sizes तक padding की आवश्यकता होती है (compute और memory बर्बाद करना) या प्रत्येक distinct shape के लिए recompilation (performance को नष्ट करना)।¹⁸⁸
Sparse operations को SparseCore के बावजूद सीमित support मिलता है। Sparse matrix-matrix multiplication, जो scientific computing और graph neural networks में common workload है, MXU या VPU पर efficient implementations का अभाव है। Specialized SparseCore embedding tables को handle करता है लेकिन general sparse linear algebra को नहीं।¹⁸⁹
Small batch inference TPU के parallel resources को underutilize करता है। 256×256 systolic array large matrices पर thrive करता है जो grid को productive work से भरते हैं। Single-query inference में अधिकांश MACs idle रहते हैं, जो low-batch scenarios के लिए optimized GPU alternatives की तुलना में per-query latency और cost खराब देता है।¹⁹⁰
Irregular computation patterns systolic array efficiency को defeat करते हैं। Unpredictable branching, recursive structures, या pointer-chasing memory access वाले algorithms में TPU performance खराब होती है क्योंकि fixed dataflow runtime-dependent behavior के अनुकूल नहीं हो सकता।¹⁹¹
Non-ML workloads शायद ही कभी TPU acceleration से लाभ उठाते हैं। Scientific simulations, video encoding, blockchain verification, और rendering सभी matrix operations के लिए TPU के higher peak FLOPs के बावजूद GPUs के अधिक general architecture पर तेज़ चलते हैं।¹⁹²
Debugging और Development Tooling Gaps
NVIDIA के ecosystem में mature profiling tools (Nsight Systems, Nsight Compute, nvprof), debuggers (cuda-gdb), और analysis frameworks शामिल हैं जो दशकों से refined हैं। TPU tooling exist करती है, लेकिन sophistication में काफी पिछड़ती है।¹⁹³
XProf TensorBoard integration के माध्यम से basic profiling प्रदान करता है लेकिन granular hardware counter access का अभाव है जो NVIDIA tools expose करते हैं। Cache miss rates, occupancy, warp divergence, या memory bank conflicts को समझना—सभी critical GPU optimization metrics—का कोई TPU equivalent नहीं है क्योंकि architecture fundamentally अलग है।¹⁹⁴
Error messages अक्सर root causes को obscure करते हैं। XLA compilation failures shape mismatches या unsupported operations के बारे में cryptic messages produce करती हैं, resolution पर कोई clear guidance नहीं। CUDA errors, unhelpfulness के लिए infamous होने के बावजूद, fifteen years के StackOverflow explanations और tribal knowledge से लाभ उठाते हैं।¹⁹⁵
Multi-chip pods पर distributed training को debug करना specialized tools के बिना impossibility के करीब पहुंचता है। Race conditions, gradient synchronization bugs, और collective operation failures non-deterministic errors के रूप में manifest होती हैं (ironically, TPU के determinism advantages के बावजूद) जो inconsistently reproduce होती हैं और systematic diagnosis का विरोध करती हैं।¹⁹⁶
Complex models के लिए iteration loop painfully extend हो जाता है। Shape changes या architecture modifications के लिए recompilation में minutes लग सकते हैं, compiler के churn करने के दौरान development को freeze कर देना। CUDA का eager execution model lower peak performance के बावजूद faster iteration enable करता है।¹⁹⁷
वास्तविक-विश्व तैनाती: बड़े पैमाने पर उत्पादन
Anthropic Claude: मल्टी-प्लेटफॉर्म रणनीति
Anthropic की अक्टूबर 2025 की घोषणा में 10 लाख से अधिक TPU चिप्स की तैनाती इतिहास में सार्वजनिक रूप से खुलासा किया गया सबसे बड़ा AI accelerator प्रतिबद्धता दर्शाती है।¹⁹⁸ कंपनी की योजना 2026 में आने वाली एक गीगावाट से भी अधिक कंप्यूट क्षमता तक पहुंचने की है, जो विशेष रूप से भविष्य के Claude मॉडल के प्रशिक्षण और सेवा के लिए है।
यह स्केल पिछली तैनातियों को कई गुणा पीछे छोड़ देता है। दस लाख चिप्स, Ironwood TPUs के रूप में कॉन्फ़िगर की गई, लगभग 4.6 exaflops FP8 कंप्यूट प्रदान करेंगी—जो केवल पांच साल पहले की संपूर्ण Top500 supercomputer सूची के कुल प्रदर्शन से 40× अधिक है।¹⁹⁹ यह प्रतिबद्धता TPU आर्किटेक्चर में frontier मॉडल विकास के लिए विश्वास दर्शाती है, जो पहले विज्ञान कथा माना जाता था।
Anthropic Google के TPUs, Amazon के Trainium, और NVIDIA GPUs में एक सुविचारित मल्टी-प्लेटफॉर्म हार्डवेयर रणनीति अपनाता है।²⁰⁰ यह विविधीकरण क्षमता बीमा, मूल्य निर्धारण लाभ, और भौगोलिक वितरण प्रदान करता है। Claude तीनों प्लेटफॉर्म की तैनातियों से विश्वव्यापी सेवा प्रदान करता है, जिसमें अनुरोध रूटिंग क्षमता उपलब्धता और क्षेत्रीय latency आवश्यकताओं पर आधारित है।
कंपनी के अगस्त 2025 के तकनीकी postmortem ने बड़े पैमाने पर तैनाती की जटिलताओं को उजागर किया। Claude API TPU सर्वर पर एक गलत कॉन्फ़िगरेशन ने token-generation त्रुटियों का कारण बना, जो कभी-कभी अंग्रेजी prompts में Thai या Chinese अक्षरों को अनपेक्षित रूप से उच्च संभावनाएं असाइन कर देता था।²⁰¹ इस घटना ने दिखाया कि साधारण त्रुटियां भी उन सिस्टम में अप्रत्याशित रूप से फैलती हैं जो दैनिक अरबों tokens संसाधित करते हैं।
एक अलग तैनाती ने XLA: TPU compiler में एक छुपे हुए bug को ट्रिगर किया जो Claude Haiku 3.5 को प्रभावित कर रहा था। यह bug महीनों तक अनदेखा रहा था जब तक कि एक विशिष्ट मॉडल आर्किटेक्चर और compiler flag संयोजन ने इस दोष को उजागर नहीं किया।²⁰² इस खोज ने जोर दिया कि production तैनाती development और staging environments से अनुपस्थित कोने के मामले पाती है।
Anthropic इंजीनियरों ने TPU की price-performance और दक्षता को प्राथमिक चयन मानदंड बताया। आकर्षक economics निश्चित बजट के भीतर बड़े experiments को सक्षम करके विकास को गति देता है।²⁰³ बड़े मॉडल का प्रशिक्षण, अधिक hyperparameter कॉन्फ़िगरेशन की खोज, और तेज़ iteration सभी प्रति-FLOP लागत कम करने से आते हैं।
Google Gemini: शुरुआत से TPU के लिए डिज़ाइन
Google के Gemini मॉडल विशेष रूप से TPUs पर प्रशिक्षित और सेवित होते हैं, जिसमें आर्किटेक्चर और प्रशिक्षण प्रक्रियाएं शुरुआत से ही TPU विशेषताओं के लिए co-designed हैं।²⁰⁴ यह तंग युग्मन TPU-विशिष्ट अनुकूलन का फायदा उठाने में सक्षम बनाता है जिसका cross-platform मॉडल लाभ नहीं उठा सकते।
Gemini तैनाती में सबसे महत्वपूर्ण मॉडल variants के प्रशिक्षण और सेवा के लिए कथित तौर पर 50,000 TPU v6e चिप्स का उपयोग होता है।²⁰⁵ इन विशाल pods के लिए परिष्कृत orchestration की आवश्यकता होती है—हजारों चिप्स में job scheduling, bottlenecks को रोकने के लिए checkpoint coordination, खोए गए काम को कम करने के लिए failure recovery, और failures के फैलने से पहले degraded nodes की पहचान के लिए real-time monitoring।
Google ने Gemini 2.0 को Trillium TPUs पर प्रशिक्षित किया, जो frontier मॉडल विकास के लिए छठी पीढ़ी के आर्किटेक्चर को validate करता है।²⁰⁶ प्रशिक्षण रन ने अभूतपूर्व चिप गिनती तक scaling दक्षता प्रदर्शित की, जहां communication overhead हावी होता है, वहां सामान्य plateaus से परे strong scaling प्राप्त की।
मॉडल serving infrastructure विशेष रूप से TPU inference optimizations का लाभ उठाती है। Batch processing कई उपयोगकर्ता अनुरोधों को एकत्रित करके MXU utilization को अधिकतम करती है। Key-value cache management HBM क्षमता का लाभ उठाती है, disk swapping के बिना long-lived context processing को सक्षम बनाती है। आर्किटेक्चर विशाल वैश्विक अनुरोध volume को संभालते हुए जटिल queries के लिए sub-second response times प्रदान करता है।²⁰⁷
Production monitoring सिस्टम लगातार 50,000+ TPUs को ट्रैक करते हैं, उन anomalies का पता लगाते हैं जो मॉडल गुणवत्ता या उपलब्धता को घटा सकती हैं।²⁰⁸ Telemetry हर चिप में error rates, latency percentiles, throughput, memory pressure, और thermal विशेषताओं को capture करती है। Machine learning मॉडल telemetry streams का खुद विश्लेषण करते हैं, failures होने से पहले उनकी भविष्यवाणी करते हैं और preemptive maintenance को trigger करते हैं।
अतिरिक्त Production तैनातियां
Midjourney GPU से TPU infrastructure में migrate हुआ, image-generation workloads के लिए 65% लागत कमी और 40% latency सुधार प्राप्त किया।²⁰⁹ Art generation सेवा peak load पर प्रति मिनट 300,000 images संसाधित करती है, जिसके लिए विशाल कंप्यूट throughput और bursty traffic patterns के तहत consistent प्रदर्शन की आवश्यकता होती है।
Cohere के language मॉडल TPU पर पिछली GPU तैनातियों की तुलना में 3× throughput प्राप्त किया।²¹⁰ यह speedup समान infrastructure footprint से अधिक ग्राहकों की सेवा करने में सक्षम बनाया, जो सीधे व्यावसायिक economics में सुधार करता है। कंपनी ने TPU pods में मॉडल को कुशलतापूर्वक parallelize करने के लिए JAX की SPMD क्षमताओं का लाभ उठाया।
Snap ने augmented reality features, recommendation systems, और creative AI tools के समर्थन में 10,000 TPU v6e चिप्स के लिए क्षमता सुरक्षित की।²¹¹ तैनाती कई भौगोलिक क्षेत्रों में फैली है, Snapchat के वैश्विक उपयोगकर्ता आधार के लिए कम latency सुनिश्चित करते हुए क्षेत्रों में मॉडल consistency बनाए रखती है।
शैक्षणिक संस्थान तेजी से अनुसंधान के लिए TPU अपना रहे हैं। TPU Research Cloud (TRC) कार्यक्रम शोधकर्ताओं को मुफ्त TPU पहुंच प्रदान करता है, ऐसे experiments को सक्षम बनाता है जो पहले केवल अच्छी तरह से वित्तपोषित कॉर्पोरेट labs के लिए सुलभ थे।²¹² यह democratization AI क्षमताओं और सीमाओं के बारे में मौलिक प्रश्नों की जांच करने वाले शिक्षाविदों के लिए हार्डवेयर बाधाओं को हटाकर वैज्ञानिक प्रगति को गति देता है।
डिबगिंग, प्रोफाइलिंग, और परफॉर्मेंस ऑप्टिमाइज़ेशन
XProf और TensorBoard इंटीग्रेशन
XProf TPU वर्कलोड्स के लिए प्राथमिक प्रोफाइलिंग टूल है, जो CPUs, GPUs, और TPUs में JAX, PyTorch/XLA, और TensorFlow प्रोग्राम्स के लिए परफॉर्मेंस एनालिसिस प्रदान करता है।²¹³ यह टूल विज़ुअलाइज़ेशन के लिए TensorBoard के साथ इंटीग्रेट होता है, प्रोफाइलिंग डेटा को जानेपहचाने इंटरफेस के माध्यम से प्रस्तुत करता है जिसे ML इंजीनियर पहले से समझते हैं।
इंस्टॉलेशन के लिए TensorBoard plugin की आवश्यकता होती है: pip install tensorboard_plugin_profile tensorboard। यह पूरी toolchain को सक्षम करता है।²¹⁴ TPU VMs पर प्रोफाइलिंग चलाने में ट्रेनिंग या इन्फरेंस के दौरान traces को कैप्चर करना, परिणामों को TensorBoard पर अपलोड करना, और bottlenecks की पहचान के लिए विज़ुअलाइज़ेशन का विश्लेषण करना शामिल है।
Overview Page उच्च-स्तरीय परफॉर्मेंस समरी metrics प्रदान करता है, जिसमें step time breakdown, device utilization, और top-level bottleneck identification शामिल है।²¹⁵ यह पेज तुरंत highlight करता है कि वर्कलोड्स compute-bound हैं (MXU लगातार चल रहा है), memory-bound हैं (HBM transfers का इंतजार कर रहे हैं), या communication-bound हैं (collective operations पर रुके हुए हैं)।
Trace Viewer और Timeline Analysis
Trace Viewer विस्तृत timeline विज़ुअलाइज़ेशन प्रदर्शित करता है जो दिखाता है कि operations कब execute होते हैं, कब data transfers होते हैं, और कहाँ idle time जमा होता है।²¹⁶ Chrome-based interface microsecond resolution तक zoom करने में सक्षम बनाता है, precise scheduling behavior को प्रकट करता है जिसे aggregate metrics छुपाते हैं।
Trace को समझने के लिए सामान्य patterns को पहचानना आवश्यक है। Operations के बीच लंबे gaps compilation overhead, data-loading bottlenecks, या poorly optimized data pipelines के कारण Python overhead का संकेत देते हैं। बार-बार छोटे operations अपर्याप्त fusion का सुझाव देते हैं। Milliseconds तक फैले collective operations communication inefficiencies या खराब sharding strategies की ओर इशारा करते हैं।²¹⁷
Color coding operation types को अलग करती है: compute के लिए हरा, memory transfers के लिए नीला, communication के लिए नारंगी, और idle time के लिए लाल। Optimized वर्कलोड्स minimal लाल gaps के साथ घनी पैक की गई रंगीन blocks दिखाते हैं। Poorly optimized code sparse timelines प्रदर्शित करता है जिसमें लंबे लाल stretches होते हैं जो wasted resources का संकेत देते हैं।²¹⁸
Advanced usage में timeline behavior को source code के साथ correlate करना शामिल है। PyTorch/XLA code में डाले गए user annotations का समर्थन करता है जो traces में दिखाई देते हैं, performance behavior को specific model components के साथ map करने में सक्षम बनाता है।²¹⁹ Annotations opaque traces को actionable insights में transform करते हैं कि किन layers या operations को optimization focus की आवश्यकता है।
Memory Profile Tool और OOM Debugging
Out-of-memory (OOM) errors बड़े model development को परेशान करते हैं। Memory Profile Tool execution के दौरान device memory usage की निगरानी करता है, peak utilization और allocation patterns को capture करता है जो OOM failures का कारण बनते हैं।²²⁰
यह टूल समय के साथ memory consumption को visualize करता है, दिखाता है कि कौन से tensors सबसे अधिक capacity consume करते हैं और कब peak usage होता है। Visualization अक्सर surprising allocations को reveal करता है—अपेक्षा से बड़े gradient buffers, activation memory जिसे checkpoint करना चाहिए, या temporary tensors जिन्हें XLA eliminate करने में असफल रहा।²²¹
Debugging strategy में कई techniques के माध्यम से memory footprint को iteratively कम करना शामिल है। Gradient checkpointing activations को store करने के बजाय backward passes के दौरान recompute करता है। Optimizer state sharding Adam momentum और variance को devices में distribute करता है। Mixed precision FP32 की तुलना में 2× memory कम करता है। Microbatching एक बड़े batch के बजाय छोटे batches को sequentially process करता है।²२२
Advanced memory optimization के लिए compiler decisions को समझना आवश्यक है। xla_dump_to flag intermediate representations को export करता है जो दिखाता है कि XLA ने computation graph को कैसे transform किया। IR का विश्लेषण reveal करता है कि क्या fusion succeed हुआ, कहाँ unnecessary copies होती हैं, और कौन से operations अपेक्षा से अधिक memory allocate करते हैं।²²³
Input Pipeline Analyzer
CPU preprocessing अक्सर TPU training में bottleneck बनती है। Input Pipeline Analyzer identify करता है कि क्या data loading accelerator consumption के साथ pace रखता है या क्या TPUs batches का इंतजार करते हुए idle बैठते हैं।²²⁴
यह टूल host-side analysis (CPU preprocessing, data augmentation, batch assembly) को device-side execution (वास्तविक TPU computation) से अलग करता है। Input-bound workloads data loading के दौरान device utilization गिरता दिखाते हैं जबकि CPU utilization peak करता है। Compute-bound workloads CPU के comfortably pace रखने के साथ उच्च device utilization maintain करते हैं।²²⁵
Optimization strategies bottleneck location पर निर्भर करती हैं। Slow host preprocessing अधिक CPU cores में data loading को parallelize करने, per-sample augmentation complexity को कम करने, या consumption से ahead batches को prefetch करने से लाभ उठाती है। Device-side bottlenecks के लिए data pipeline tuning के बजाय model architecture में changes, बेहतर fusion, या sharding adjustments की आवश्यकता होती है।²²⁶
## Tensor Processing Units का भविष्य
Google का सात-पीढ़ी का architectural evolution विशेषीकृत AI accelerators में निरंतर नवाचार को दर्शाता है। Ironwood का FP8 support, विशाल memory capacity, और 9,216-chip superpod scaling भविष्य के विकास की दिशाओं का सुझाव देती है।²²⁷
Precision reduction का चलन संभवतः FP4 या विशिष्ट operations के लिए इससे भी कम तक जारी रहेगा। नई research यह दर्शाती है कि कई neural network operations सावधानीपूर्वक training procedures के साथ extreme quantization को सहन करते हैं। भविष्य के TPUs में FP4 forward passes, FP8 backward passes, और FP32 optimizer updates के साथ mixed-precision systems को implement किया जा सकता है।²²⁸
Memory capacity model size की वृद्धि के साथ एक race में है। वर्तमान frontier models पहले से ही accelerator memory पर दबाव डालते हैं, जिसके लिए sophisticated parallelism strategies की आवश्यकता होती है। अगली पीढ़ी के TPUs में 3D XPoint या resistive RAM जैसी non-volatile memory technologies को integrate किया जा सकता है, जो DRAM के power consumption के बिना terabyte-scale on-package memory को सक्षम बनाएगी।²²⁹
Optical interconnects circuit switching से आगे बढ़कर optical computing elements को भी शामिल कर सकते हैं। Research photonic matrix multiplication को explore करती है जो light speed पर minimal power के साथ execute होती है, जो विशिष्ट operations के लिए optical co-processors के साथ electronic systolic arrays को संभावित रूप से augment कर सकती है।²३⁰
Sparsity support संभवतः embeddings से आगे बढ़कर general sparse linear algebra तक विस्तृत होगा। Neural network pruning techniques यह दर्शाती हैं कि 90%+ weights को quality के नुकसान के बिना zero out किया जा सकता है। भविष्य की architectures zero-valued computations को explicitly compute करके discard करने के बजाय natively skip कर सकती हैं।²३¹
TPU success के मूलभूत architectural principles—domain specialization, custom interconnect, co-designed software stacks, और building-scale orchestration—तेजी से specialized accelerators के भविष्य की ओर इशारा करते हैं। One-size-fits-all processors के बजाय, हमें training versus inference, convolutional networks versus transformers, dense versus sparse models, और short versus long sequences के लिए optimized accelerators दिख सकते हैं।²३²
आज AI infrastructure बनाने वाले engineers को TPU architecture की गहरी समझ होनी चाहिए। चाहे Google Cloud पर deploy करना हो, accelerator market में Google के साथ compete करना हो, या next-generation ML systems design करना हो, TPU में embodied design principles और tradeoffs AI workloads की hardware से demands के बारे में fundamental truths को reveal करते हैं। Systolic array mathematics, memory hierarchy design, interconnect topology, और compiler optimization strategies decades के accumulated wisdom को represent करती हैं जो TPU से कहीं आगे तक applicable है।
Specialization और generality के बीच tension जो TPU versus GPU को define करती है, वह indefinitely तक बनी रहेगी। TPUs narrow workloads पर extreme efficiency के लिए flexibility को sacrifice करते हैं। GPUs broader applicability के लिए peak efficiency को sacrifice करते हैं। कोई भी approach dominate नहीं करती—optimal choice पूरी तरह workload characteristics, scale, cost constraints, और operational requirements पर depend करती है। Scale पर AI के साथ succeed करने वाले organizations तेजी से heterogeneous strategies अपना रहे हैं, single platform पर standardize करने के बजाय workload demands के साथ accelerator architectures को match कर रहे हैं।
Anthropic का TPU के लिए million-chip commitment यह demonstrate करता है कि architecture ने highest scales पर production maturity हासिल कर ली है। 2026 में online आने वाली multi-gigawatt deployments उन models को train करेंगी जो AI की achieve करने की सीमाओं को push करती हैं, और उन models को enable करने वाली infrastructure engineering sophistication को embody करती है जिसे few organizations ने match किया है। यह समझना कि एक systolic array में 65,536 multiply-accumulate units कैसे frontier models को train करने के लिए collaborate करते हैं, AI के भविष्य के बारे में serious किसी भी व्यक्ति के लिए महत्वपूर्ण है।
संदर्भ
-
Google Cloud Press Corner, "Anthropic to Expand Use of Google Cloud TPUs and Services," October 23, 2025, https://www.googlecloudpresscorner.com/2025-10-23-Anthropic-to-Expand-Use-of-Google-Cloud-TPUs-and-Services.
-
TrendForce, "Google Unveils 7th-Gen TPU Ironwood with 9,216-Chip Superpod, Taking Aim at NVIDIA," November 7, 2025, https://www.trendforce.com/news/2025/11/07/news-google-unveils-7th-gen-tpu-ironwood-with-9216-chip-superpod-taking-aim-at-nvidia/.
-
Norman P. Jouppi et al., "TPU v4: An Optically Reconfigurable Supercomputer for Machine Learning with Hardware Support for Embeddings," in Proceedings of the 50th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture (2023), arXiv:2304.01433.
-
Anthropic, "Expanding our use of Google Cloud TPUs and Services," Anthropic News, October 2025, https://www.anthropic.com/news/expanding-our-use-of-google-cloud-tpus-and-services.
-
Google Cloud Blog, "Quantifying the performance of the TPU, our first machine learning chip," April 2017, https://cloud.google.com/blog/products/gcp/quantifying-the-performance-of-the-tpu-our-first-machine-learning-chip.
-
Norman P. Jouppi et al., "In-Datacenter Performance Analysis of a Tensor Processing Unit," Proceedings of the 44th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture (2017), arXiv:1704.04760.
-
Jouppi et al., "In-Datacenter Performance Analysis."
-
Jouppi et al., "In-Datacenter Performance Analysis."
-
Jonathan Hui, "AI Chips: Google TPU," Medium, accessed December 2025, https://jonathan-hui.medium.com/ai-chips-tpu-3fa0b2451a2d.
-
Wikipedia, "Bfloat16 floating-point format," accessed December 2025, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bfloat16_floating-point_format.
-
Henry Ko, "TPU Deep Dive," व्यक्तिगत ब्लॉग, accessed December 2025, https://henryhmko.github.io/posts/tpu/tpu.html.
-
Wikipedia, "Tensor Processing Unit," accessed December 2025, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tensor_Processing_Unit.
-
Wikipedia, "Tensor Processing Unit."
-
Wikipedia, "Tensor Processing Unit."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Jouppi et al., "TPU v4: An Optically Reconfigurable Supercomputer."
-
Jouppi et al., "TPU v4: An Optically Reconfigurable Supercomputer."
-
Jouppi et al., "TPU v4: An Optically Reconfigurable Supercomputer."
-
Jouppi et al., "TPU v4: An Optically Reconfigurable Supercomputer."
-
OpenXLA Project, "A deep dive into SparseCore for Large Embedding Models (LEM)," accessed December 2025, https://openxla.org/xla/sparsecore.
-
JAX Scaling Guide, "How to Think About TPUs," accessed December 2025, https://jax-ml.github.io/scaling-book/tpus/.
-
JAX Scaling Guide, "How to Think About TPUs."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
JAX Scaling Guide, "How to Think About TPUs."
-
Google Cloud Blog, "Introducing Trillium, sixth-generation TPUs," May 2024, https://cloud.google.com/blog/products/compute/introducing-trillium-6th-gen-tpus.
-
Google Cloud Blog, "Introducing Trillium."
-
Google Cloud Blog, "Introducing Trillium."
-
Google Cloud Blog, "Introducing Trillium."
-
Google Cloud Blog, "Introducing Trillium."
-
Google Blog, "Ironwood: The first Google TPU for the age of inference," November 2025, https://blog.google/products/google-cloud/ironwood-tpu-age-of-inference/.
-
XPU.pub, "Google Adds FP8 to Ironwood TPU; Can It Beat Blackwell?" April 16, 2025, https://xpu.pub/2025/04/16/google-ironwood/.
-
TrendForce, "Google Unveils 7th-Gen TPU Ironwood."
-
The Register, "Google's 7th-gen Ironwood TPUs promise 42 AI exaFLOPS pods," April 10, 2025, https://www.theregister.com/2025/04/10/googles_7thgen_ironwood_tpus_debut/.
-
TrendForce, "Google Unveils 7th-Gen TPU Ironwood."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
XPU.pub, "Google Adds FP8 to Ironwood TPU."
-
Google Cloud Press Corner, "Anthropic to Expand Use."
-
Telesens, "Understanding Matrix Multiplication on a Weight-Stationary Systolic Architecture," July 30, 2018, https://telesens.co/2018/07/30/systolic-architectures/.
-
Telesens, "Understanding Matrix Multiplication."
-
Jouppi et al., "In-Datacenter Performance Analysis."
-
Telesens, "Understanding Matrix Multiplication."
-
CP Lu, "Should We All Embrace Systolic Arrays?" Medium, accessed December 2025, https://cplu.medium.com/should-we-all-embrace-systolic-array-df3830f193dc.
-
Google Cloud Documentation, "TPU architecture," accessed December 2025, https://docs.cloud.google.com/tpu/docs/system-architecture-tpu-vm.
-
Google Cloud Documentation, "TPU architecture."
-
Hui, "AI Chips: Google TPU."
-
Telnyx, "Architecture insights: MXU and TPU components," accessed December 2025, https://telnyx.com/learn-ai/mxu-tpu.
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Jouppi et al., "TPU v4: An Optically Reconfigurable Supercomputer."
-
SemiEngineering, "Tensor Processing Unit (TPU)," accessed December 2025, https://semiengineering.com/knowledge_centers/integrated-circuit/ic-types/processors/tensor-processing-unit-tpu/.
-
TrendForce, "Google Unveils 7th-Gen TPU Ironwood."
-
SemiEngineering, "Tensor Processing Unit (TPU)."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Google Cloud Documentation, "Cloud TPU performance guide," accessed December 2025, https://cloud.google.com/tpu/docs/performance-guide.
-
OpenXLA Project, "A deep dive into SparseCore."
-
OpenXLA Project, "A deep dive into SparseCore."
-
OpenXLA Project, "A deep dive into SparseCore."
-
Jouppi et al., "TPU v4: An Optically Reconfigurable Supercomputer."
-
OpenXLA Project, "A deep dive into SparseCore."
-
Jouppi et al., "TPU v4: An Optically Reconfigurable Supercomputer."
-
OpenXLA Project, "A deep dive into SparseCore."
-
JAX Scaling Guide, "How to Think About TPUs."
-
JAX Scaling Guide, "How to Think About TPUs."
-
JAX Scaling Guide, "How to Think About TPUs."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
JAX Scaling Guide, "How to Think About TPUs."
-
JAX Scaling Guide, "How to Think About TPUs."
-
TrendForce, "Google Unveils 7th-Gen TPU Ironwood."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Anthropic, "Expanding our use of Google Cloud TPUs."
-
Jouppi et al., "TPU v4: An Optically Reconfigurable Supercomputer."
-
Jouppi et al., "TPU v4: An Optically Reconfigurable Supercomputer."
-
Jouppi et al., "TPU v4: An Optically Reconfigurable Supercomputer."
-
Jouppi et al., "TPU v4: An Optically Reconfigurable Supercomputer."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Jouppi et al., "TPU v4: An Optically Reconfigurable Supercomputer."
-
Leon Poutievski, "Mission Apollo: Landing Optical Circuit Switching at Datacenter Scale," LinkedIn, June 2022, https://www.linkedin.com/posts/leon-poutievski-8910a851_mission-apollo-landing-optical-circuit-switching-activity-6968472071534235649-cB4l.
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Jouppi et al., "TPU v4: An Optically Reconfigurable Supercomputer."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Jouppi et al., "TPU v4: An Optically Reconfigurable Supercomputer."
-
JAX Scaling Guide, "How to Think About TPUs."
-
TrendForce, "Google Unveils 7th-Gen TPU Ironwood."
-
TrendForce, "Google Unveils 7th-Gen TPU Ironwood."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
OpenXLA Project, "XLA: Optimizing Compiler for Machine Learning," accessed December 2025, https://openxla.org/xla.
-
Daniel Snider and Ruofan Liang, "Operator Fusion in XLA: Analysis and Evaluation," शैक्षणिक पेपर, accessed December 2025, https://danielsnider.ca/papers/Operator_Fusion_in_XLA_Analysis_and_Evaluation.pdf.
-
Snider and Liang, "Operator Fusion in XLA."
-
APXML, "Memory-Aware Data Layout Transformations (NCHW/NHWC)," accessed December 2025, https://apxml.com/courses/compiler-runtime-optimization-ml/chapter-3-advanced-graph-level-optimizations/memory-aware-layout-transformations.
-
OpenXLA Project, "XLA."
-
PyTorch Documentation, "Pytorch/XLA Overview," accessed December 2025, https://docs.pytorch.org/xla/master/learn/xla-overview.html.
-
OpenXLA Project, "A deep dive into SparseCore."
-
Mangpo Phothilimthana et al., "A Flexible Approach to Autotuning Multi-Pass Machine Learning Compilers," PACT 2021, accessed December 2025, https://mangpo.net/papers/xla-autotuning-pact2021.pdf.
-
JAX Documentation, "Introduction to parallel programming," accessed December 2025, https://docs.jax.dev/en/latest/sharded-computation.html.
-
GitHub, "jax-ml/jax: Composable transformations of Python+NumPy programs," accessed December 2025, https://github.com/jax-ml/jax.
-
OpenXLA Project, "Shardy Guide for JAX Users," accessed December 2025, https://openxla.org/shardy/getting_started_jax.
-
JAX Documentation, "Introduction to parallel programming."
-
OpenXLA Project, "Shardy Guide for JAX Users."
-
OpenXLA Project, "Shardy Guide for JAX Users."
-
JAX Documentation, "Introduction to parallel programming."
-
OpenXLA Project, "Shardy Guide for JAX Users."
-
PyTorch Documentation, "Pytorch/XLA Overview."
-
GitHub, "RFC: Evolving PyTorch/XLA for a more native experience on TPU," Issue #9684, accessed December 2025, https://github.com/pytorch/xla/issues/9684.
-
Google Cloud Blog, "PyTorch/XLA 2.4 improves Pallas and adds 'eager mode,'" accessed December 2025, https://cloud.google.com/blog/products/ai-machine-learning/pytorch-xla-2-4-improves-pallas-and-adds-eager-mode/.
-
PyTorch Documentation, "Pytorch/XLA Overview."
-
PyTorch Documentation, "Custom Kernels via Pallas," accessed December 2025, https://docs.pytorch.org/xla/master/features/pallas.html.
-
PyTorch Documentation, "Custom Kernels via Pallas."
-
PyTorch Documentation, "Custom Kernels via Pallas."
-
vLLM Blog, "vLLM TPU: A New Unified Backend Supporting PyTorch and JAX on TPU," October 16, 2025, https://blog.vllm.ai/2025/10/16/vllm-tpu.html.
-
GitHub, "pytorch/xla," accessed December 2025, https://github.com/pytorch/xla.
-
StackGpu, "FP8, BF16, and INT8: How Low-Precision Formats Are Revolutionizing Deep Learning Throughput," Medium, accessed December 2025, https://medium.com/@StackGpu/fp8-bf16-and-int8-how-low-precision-formats-are-revolutionizing-deep-learning-throughput-e6c1f3adabc2.
-
Wikipedia, "Bfloat16 floating-point format."
-
Wikipedia, "Bfloat16 floating-point format."
-
Paulius Micikevicius et al., "FP8 Formats for Deep Learning," arXiv:2209.05433, September 2022.
-
XPU.pub, "Google Adds FP8 to Ironwood TPU."
-
Micikevicius et al., "FP8 Formats for Deep Learning."
-
Google Cloud Blog, "Accurate Quantized Training (AQT) for TPU v5e," accessed December 2025, https://cloud.google.com/blog/products/compute/accurate-quantized-training-aqt-for-tpu-v5e.
-
StackGpu, "FP8, BF16, and INT8."
-
Jeffrey Tse, "Understanding the FP64, FP32, FP16, BFLOAT16, TF32, FP8 Formats," व्यक्तिगत ब्लॉग, December 9, 2024, https://jeffreytse.net/computer/2024/12/09/understanding-the-fp64-fp32-fp16-bfloat16-tf32-fp8-formats.html.
-
PyTorch Blog, "PyTorch/XLA SPMD: Scale Up Model Training and Serving with Automatic Parallelization," accessed December 2025, https://pytorch.org/blog/pytorch-xla-spmd/.
-
OpenXLA Project, "Shardy Guide for JAX Users."
-
JAX Documentation, "Introduction to parallel programming."
-
OpenXLA Project, "Shardy Guide for JAX Users."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
JAX Documentation, "Introduction to parallel programming."
-
Anthropic, "Expanding our use of Google Cloud TPUs."
-
JAX Documentation, "Introduction to parallel programming."
-
JAX Documentation, "Introduction to parallel programming."
-
Adam Roberts et al., "Scaling Up Models and Data with t5x and seqio," arXiv:2203.17189, March 2022.
-
Roberts et al., "Scaling Up Models and Data."
-
JAX Documentation, "Introduction to parallel programming."
-
JAX Documentation, "Introduction to parallel programming."
-
OpenXLA Project, "Shardy Guide for JAX Users."
-
Roberts et al., "Scaling Up Models and Data."
-
Roberts et al., "Scaling Up Models and Data."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
MLCommons, "Benchmark MLPerf Training," accessed December 2025, https://mlcommons.org/benchmarks/training/.
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
HPCwire, "MLPerf Training v5.0 Benchmark Results Reflect Rapid Growth in the Field of AI," June 2025, https://www.hpcwire.com/off-the-wire/mlperf-training-v5-0-benchmark-results-reflect-rapid-growth-in-the-field-of-ai/.
-
MLCommons, "MLCommons Releases New MLPerf Inference v5.0 Benchmark Results," April 2025, https://mlcommons.org/2025/04/mlperf-inference-v5-0-results/.
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Google Cloud Blog, "TPU v4 enables performance, energy and CO2e efficiency gains," accessed December 2025, https://cloud.google.com/blog/topics/systems/tpu-v4-enables-performance-energy-and-co2e-efficiency-gains.
-
TrendForce, "Google Unveils 7th-Gen TPU Ironwood."
-
Google Cloud Blog, "Quantifying the performance of the TPU."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Artech Digital, "Energy-Efficient GPU vs. TPU Allocation," accessed December 2025, https://www.artech-digital.com/blog/energy-efficient-gpu-vs-tpu-allocation.
-
Wikipedia, "Tensor Processing Unit."
-
XPU.pub, "Google Adds FP8 to Ironwood TPU."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Google Cloud Blog, "TPU v4 enables performance, energy and CO2e efficiency gains."
-
ByteBridge, "GPU and TPU Comparative Analysis Report," Medium, accessed December 2025, https://bytebridge.medium.com/gpu-and-tpu-comparative-analysis-report-a5268e4f0d2a.
-
ByteBridge, "GPU and TPU Comparative Analysis Report."
-
Anthropic, "Expanding our use of Google Cloud TPUs."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
DataCamp, "Understanding TPUs vs GPUs in AI: A Comprehensive Guide," accessed December 2025, https://www.datacamp.com/blog/tpu-vs-gpu-ai.
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
DataCamp, "Understanding TPUs vs GPUs in AI."
-
Grigory Sapunov, "FP64, FP32, FP16, BFLOAT16, TF32, and other members of the ZOO," Medium, accessed December 2025, https://moocaholic.medium.com/fp64-fp32-fp16-bfloat16-tf32-and-other-members-of-the-zoo-a1ca7897d407.
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Snider and Liang, "Operator Fusion in XLA."
-
APXML, "Memory-Aware Data Layout Transformations."
-
Google Cloud Blog, "How Lightricks trains video diffusion models at scale with JAX on TPU," accessed December 2025, https://cloud.google.com/blog/products/media-entertainment/how-lightricks-trains-video-diffusion-models-at-scale-with-jax-on-tpu.
-
CloudOptimo, "TPU vs GPU: What's the Difference in 2025?" accessed December 2025, https://www.cloudoptimo.com/blog/tpu-vs-gpu-what-is-the-difference-in-2025/.
-
Phoenix NAP, "TPU vs. GPU: Differences Explained," accessed December 2025, https://phoenixnap.com/kb/tpu-vs-gpu.
-
CloudOptimo, "TPU vs GPU."
-
DataCamp, "Understanding TPUs vs GPUs in AI."
-
Tailscale, "TPU vs GPU: Which Is Better for AI Infrastructure in 2025?" accessed December 2025, https://tailscale.com/learn/what-is-tpu-vs-gpu.
-
DataCamp, "Understanding TPUs vs GPUs in AI."
-
DataCamp, "Understanding TPUs vs GPUs in AI."
-
PyTorch Documentation, "Custom Kernels via Pallas."
-
Phoenix NAP, "TPU vs. GPU: Differences Explained."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
OpenMetal, "TPU vs GPU: Pros and Cons," accessed December 2025, https://openmetal.io/docs/product-guides/private-cloud/tpu-vs-gpu-pros-and-cons/.
-
OpenMetal, "TPU vs GPU: Pros and Cons."
-
Phoenix NAP, "TPU vs. GPU: Differences Explained."
-
PRIMO.ai, "Processing Units - CPU, GPU, APU, TPU, VPU, FPGA, QPU," accessed December 2025, https://primo.ai/index.php?title=Processing_Units_-_CPU%2C_GPU%2C_APU%2C_TPU%2C_VPU%2C_FPGA%2C_QPU.
-
DataCamp, "Understanding TPUs vs GPUs in AI."
-
Google Cloud Documentation, "Profile your model on Cloud TPU VMs," accessed December 2025, https://cloud.google.com/tpu/docs/cloud-tpu-tools.
-
DataCamp, "Understanding TPUs vs GPUs in AI."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
GitHub, "RFC: Evolving PyTorch/XLA."
-
Google Cloud Press Corner, "Anthropic to Expand Use."
-
TrendForce, "Google Unveils 7th-Gen TPU Ironwood."
-
Maginative, "Anthropic Secures 1M Google TPUs While Keeping Amazon as Primary Training Partner," accessed December 2025, https://www.maginative.com/article/anthropic-secures-1m-google-tpus-while-keeping-amazon-as-primary-training-partner/.
-
Anthropic, "A postmortem of three recent issues," Engineering Blog, August 2025, https://www.anthropic.com/engineering/a-postmortem-of-three-recent-issues.
-
Anthropic, "A postmortem of three recent issues."
-
AI Magazine, "Why Anthropic Uses Google Cloud TPUs for AI Infrastructure," accessed December 2025, https://aimagazine.com/news/why-anthropic-uses-google-cloud-tpus-for-ai-infrastructure.
-
Google Cloud Blog, "Ironwood TPUs and new Axion-based VMs for your AI workloads," November 2025, https://cloud.google.com/blog/products/compute/ironwood-tpus-and-new-axion-based-vms-for-your-ai-workloads.
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
TrendForce, "Google Unveils 7th-Gen TPU Ironwood."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Google Cloud, "Tensor Processing Units (TPUs)," accessed December 2025, https://cloud.google.com/tpu.
-
TensorFlow Documentation, "Optimize TensorFlow performance using the Profiler," accessed December 2025, https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/profiler.
-
Google Cloud Documentation, "Profile your model on Cloud TPU VMs."
-
TensorFlow Documentation, "TensorFlow Profiler: Profile model performance," accessed December 2025, https://www.tensorflow.org/tensorboard/tensorboard_profiling_keras.
-
Google Cloud Documentation, "Profile your model on Cloud TPU VMs."
-
Google Cloud Blog, "PyTorch/XLA: Performance debugging on Cloud TPU VM: Part III," accessed December 2025, https://cloud.google.com/blog/topics/developers-practitioners/pytorchxla-performance-debugging-cloud-tpu-vm-part-iii.
-
Google Cloud Blog, "PyTorch/XLA: Performance debugging Part III."
-
Google Cloud Documentation, "Profile PyTorch XLA workloads," accessed December 2025, https://docs.cloud.google.com/tpu/docs/pytorch-xla-performance-profiling-tpu-vm.
-
TensorFlow Documentation, "Optimize TensorFlow performance using the Profiler."
-
TensorFlow Documentation, "Optimize TensorFlow performance using the Profiler."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Google Cloud Documentation, "Cloud TPU performance guide."
-
TensorFlow Documentation, "Optimize TensorFlow performance using the Profiler."
-
TensorFlow Documentation, "Optimize TensorFlow performance using the Profiler."
-
TensorFlow Documentation, "Optimize TensorFlow performance using the Profiler."
-
TrendForce, "Google Unveils 7th-Gen TPU Ironwood."
-
Tse, "Understanding the FP64, FP32, FP16, BFLOAT16, TF32, FP8 Formats."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."
-
Ko, "TPU Deep Dive."



